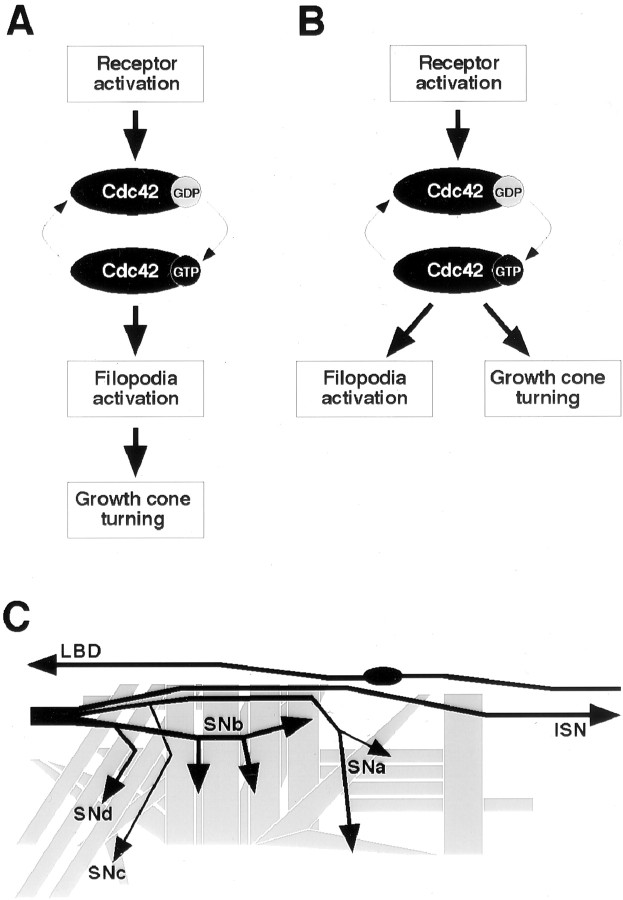
Fig. 1.
Models of Cdc42 activation. During its activation, Cdc42 switches from a GDP-bound inactive state to a GTP-bound active state (thin arrows). A, In the linear pathway model, the GTP-bound Cdc42 binds to downstream effectors, controlling filopodial activity and, as a direct consequence, leading to directed growth cone navigation. B, In the parallel pathways model, Cdc42 activation initiates several separate downstream events, with one being responsible for filopodial activation and the other regulating cytoskeletal and membrane dynamics during growth cone turning. Arrows do not necessarily indicate direct signaling but rather hierarchical events. C, Stereotyped motor and sensory axon pathways in the Drosophilaembryo. In each abdominal half-segment, the motoneuron axons are grouped into five nerves (ISN, SNa,SNb, SNc, andSNd). The LBD sensory neuron extends an afferent axon (LBD) via its own pathway near the segment border into the CNS. The CNS is to the left, and nine distal (dorsal) muscle cells are not shown.