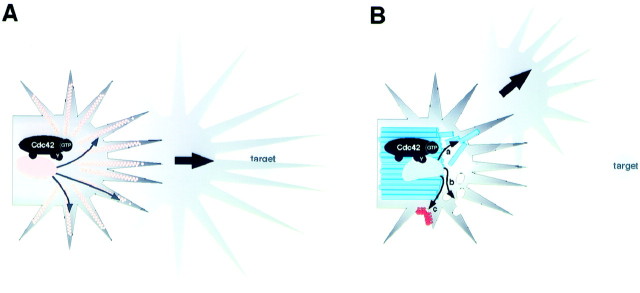
Fig. 8.
Roles of Cdc42 in a growth cone. A, Cdc42 activation in some growth cones (LBD growth cones) enhances filopodia activity. An effector(s) (oval shape) binds to the GTP-bound Cdc42 and stimulates (arrows inside the growth cone) actin polymerization (peach color) in filopodia. Despite increased length, extension, and retraction rates of filopodia, the growth cone still responds to cues from atarget and navigates normally (Figs. 4, 5).B, In other growth cones (SNb growth cones), activated Cdc42 associates with alternative effector(s) (mushroom-head shape). This association involves a Cdc42 microdomain distinct from that involved in binding to the filopodia-controlling effector(s) (compare with A). The subsequent activation of the alternative effector does not alter the filopodial activity but instead changes microtubule (blue) (a), membrane (b), and cell surface adhesion dynamics in the growth cone (see Discussion for other possibilities). With such an out-of-context alteration of cytoplasmic dynamics, the growth cone turns incorrectly at a random site without an increase in filopodial activity (Figs. 3, 6).