Figure 1: Inflammatory bowel disease and the microbiota.
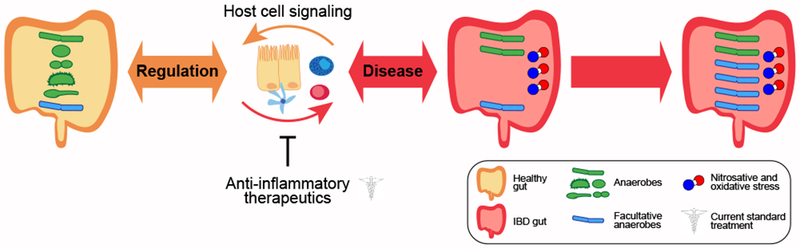
In health, gut bacterial composition (anaerobes and facultative anaerobes) is maintained in balance with host cell physiology. Alterations in gut microbiome composition during disease include reduced microbial diversity and expansion of facultative anaerobes due to increased nitrosative and oxidative stress in the gut. Current standard treatments, such as 5ASA mesalamine, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and anti-TNFα biologic therapy, focus on treating and controlling disease symptoms, in particular chronic inflammation.
