Figure 3. Microbiome-based therapies for inflammatory bowel disease.
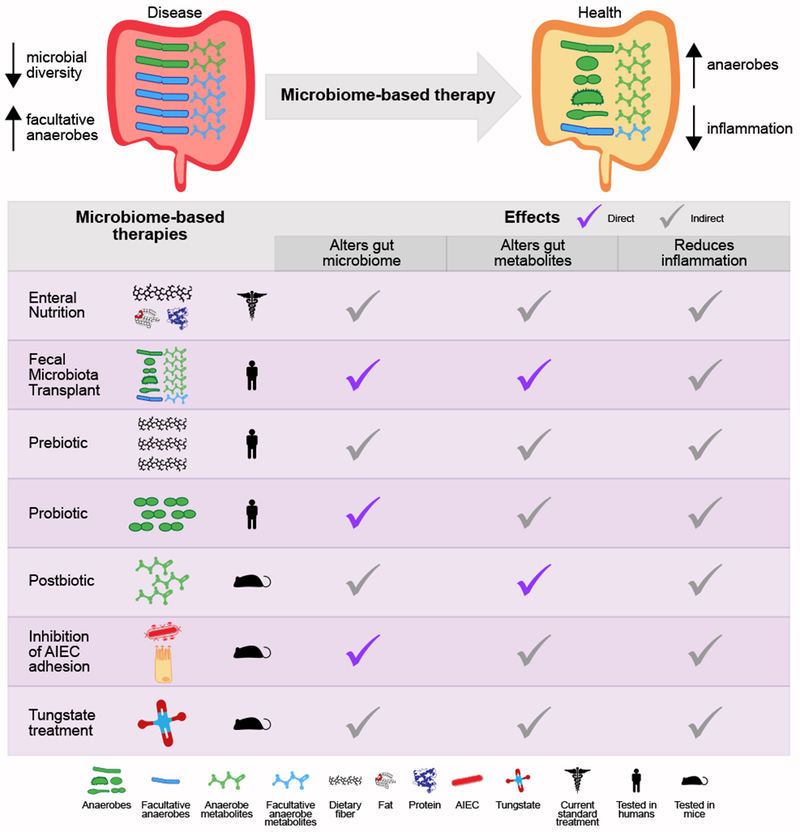
Microbiome-based therapies for inflammatory bowel disease aim to restore the gut microbial balance, which includes increasing microbial diversity, in particular anaerobic bacteria, reducing facultative anaerobes, and reducing gut inflammation (part a). Current and developing treatments either alter nutrition, administer microbial organisms and/or metabolites, or directly target microorganisms and/or pathways (part b). The effects of these treatments, including reduction of gut inflammation and alterations of the gut microbial communities and metabolites, are either direct or indirect. AIEC, adhesive invasive Escherichia coli.
