Figure 1.
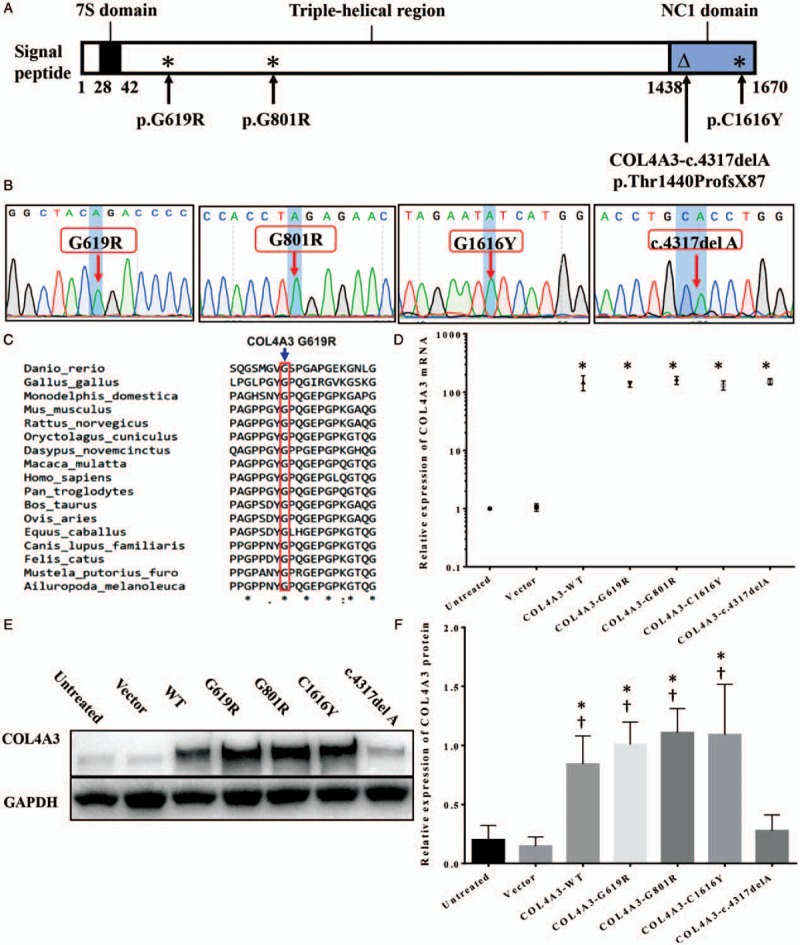
COL4A3 expression in WT and COL4A3-G619R, -G801R, -C1616Y, and c.4317delA (p.Thr1440ProfsX87) mutant transfected human podocyte cells. (A) Specific position of each COL4A3 mutation site in the COL4A3 protein that indicates the c.4317delA mutation was different from the others; it was a frameshift mutation at the DNA level that caused a truncated mutation in the protein level; (B) COL4A3 mutants constructed by lentivirus were confirmed using Sanger sequencing; (C) Evolutionary conservation analysis of the COL4A3 G619R mutation site. (D) Quantitative PCR detected COL4A3 mRNA expression levels in human podocyte cells stably transfected with different COL4A3 lentiviruses (∗compared to the empty vector group, P < 0.05); (E) Western blotting evaluated COL4A3 protein expression in human podocytes after transfection by different COL4A3 lentiviruses. The expression level of the COL4A3 c.4317delA (truncated mutation) group had an obviously lower COL4A3 protein level, unlike the WT, G619R, G801R, and C1616Y groups. (F) Three independent repetitions of COL4A3 protein expression experiment in different groups confirmed that the COL4A3 levels were differed significantly between the WT and c.4317delA groups (∗compared to the WT group, †compared to the c.4317delA group, P < 0.05). PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; WT: Wild-type.
