Figure 5.
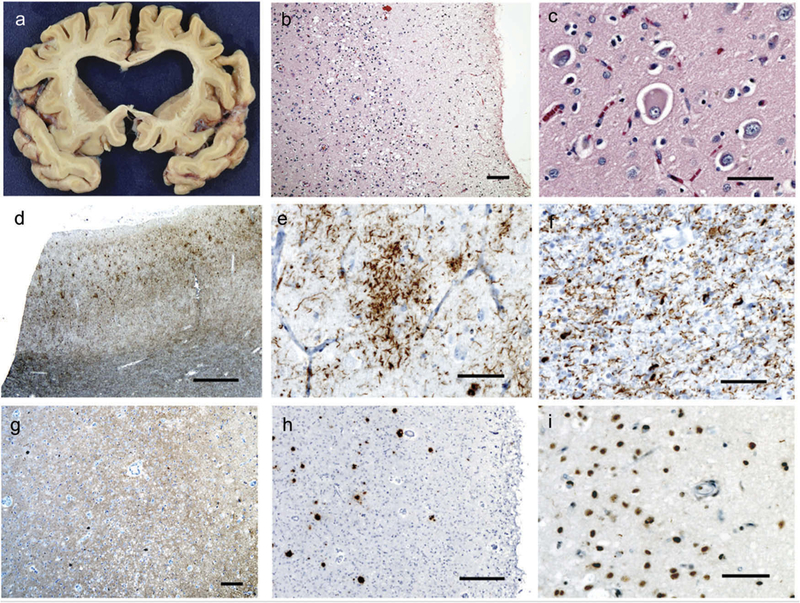
Neuropathology. On gross pathology (a), there was diffuse cortical atrophy, most prominent in the insula, inferior frontal gyrus, and superior temporal gyrus with associated ex-vacuo dilatation of the lateral ventricles. On hematoxylin and eosin staining, there were nonspecific signs of neurodegeneration, including superficial astrogliosis and microvacuolation (b). Balloon cells were frequently identified in the cortex (c). Immunohistochemical staining for phosphorylated tau protein demonstrated abundant deposition, including prominent white matter staining in addition to the cytoplasmic accumulations noted in the cortex (d), frequent astrocytic plaques (f), and numerous white matter threads and coiled bodies (f), consistent with corticobasal degeneration. A 3-repeat tau immunostain was notable for scattered neurofibrillary tangles in the cortex (g), and frequent beta-amyloid-positive plaques were also present (h), indicating the presence of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Finally, TDP-43-positive cytoplasmic inclusions and threads consistent with a TDP-43-type A pattern of FTLD were also identified (i). Scale bars are as follows: B – 100 microns, C – 50 microns, D – 1 mm, E – 50 microns, F – 50 microns, G – 100 microns, H – 250 microns, I – 50 microns.
