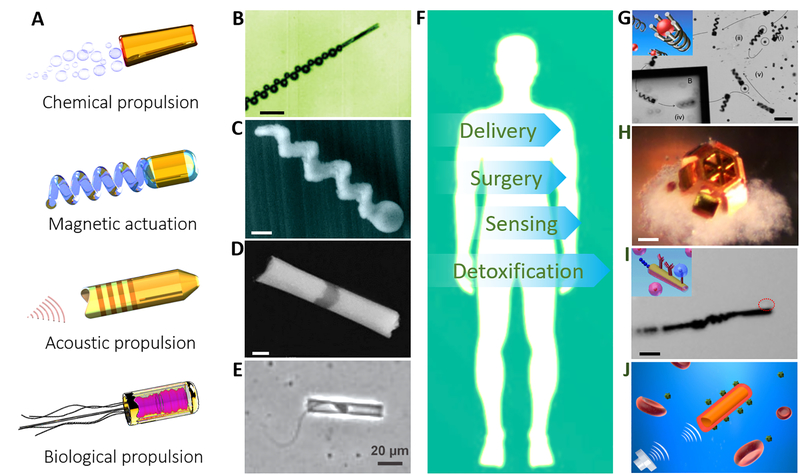
Fig. 1. Actuation mechanisms and potential biomedical applications of various types of micro/nanorobots.
(A) Typical propulsion mechanisms of micro/nanoscale robots. (B) Chemically powered microrocket (30). Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Magnetically actuated helical nanoswimmer (31). Scale bar: 200 nm. (D) Acoustically propelled nanowire motor (32). Scale bar: 200 nm. (E) Biologically propelled sperm hybrid microrobot (33). (F) Potential biomedical applications of nanorobots. (G) Magnetic helical microrobot for cargo delivery (38). Scale bar: 50 μm. (H) Micro-grippers for high precision surgery (39). Scale bar: 100 μm. (I) Antibody-immobilized microrobot for sensing and isolating cancer cells (40). Scale bar: 30 μm. (J) Red blood cell (RBC) membrane-coated nanomotor for biodetoxification (41).