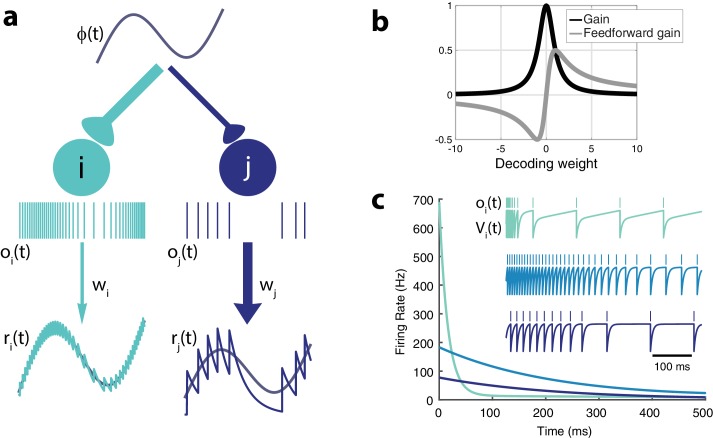
Figure 2. Intrinsic model neuron properties.
(a) High gain neurons (light blue) are intrinsically excitable and due to their small decoding weights they are precise while low gain neurons (dark blue) are less excitable and less precise. An arbitrary input, , elicits distinct responses from the two neurons (spikes train and , respectively). Neurons send a filtered response, , , to the decoder weighted by and , respectively. (b) Relationship between gain , feedforward gain , and decoding weight (). (c) Different gains give neurons distinct adaptation dynamics. Instantaneous spiking rates in response to a constant input are plotted over time for three model neurons with different decoding weights (light blue, w = 1; medium blue, w = 5; dark blue, w = 9). High gain neurons have the steepest adaptation (light blue) whereas low gain neurons (dark blue) do not adapt as rapidly given the same input. Inset shows the voltage trace, , and spike train, , for each example neuron.