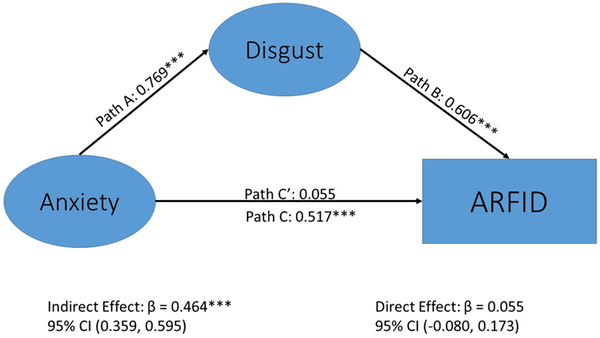
Figure 3.
Mediation model of disgust as a significant mediator of the association between anxiety and Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder diagnosis†
Standardized weights are shown. N=1644. The direct path from anxiety to ARFID diagnosis (β=.517, p < .001) becomes non-significant with the addition of disgust as a mediator (β=.055, p = .406). The indirect path of anxiety mediated by disgust was significant, β=.465, p < .001. Abbreviations: disgnew = disgust to a new food; disgdis = disgust to a disliked food; gagnew = gagging to a new food; gagdis = gagging to a disliked food; anxnew = anxiety to a new food; anxdis = anxiety to a disliked food; disgust = disgust latent factor; anxiety = anxiety latent factor; arfiddx = do you have a diagnosis of avoidant restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID; yes/no response). *** = p < .001. †See Table 3 for results with Picky Eating as the outcome.