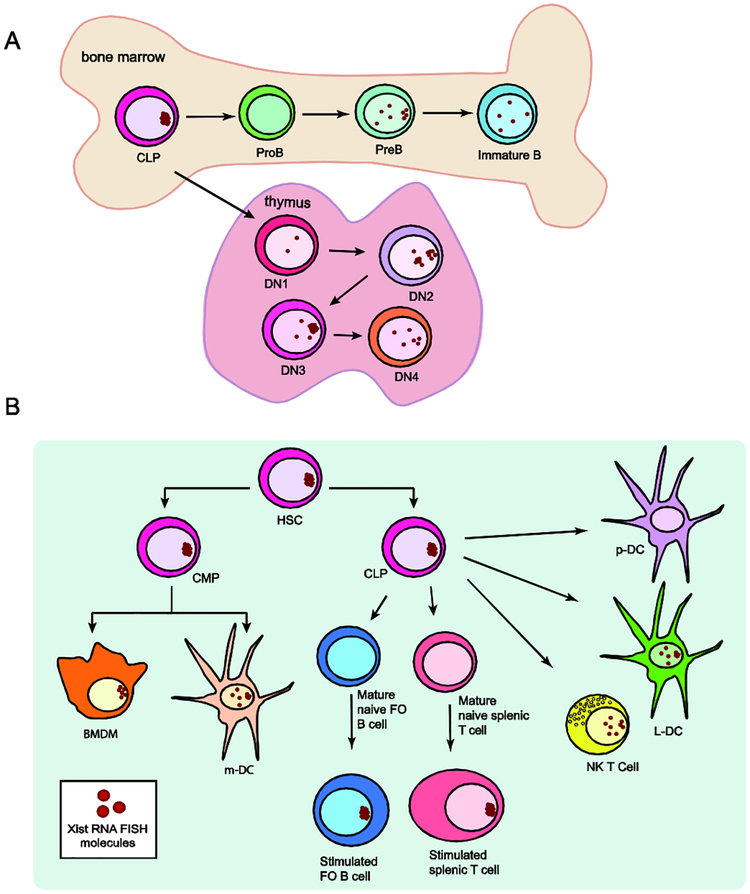
Figure 1: Xist RNA is dynamically localized to the Xi in developing lymphocytes and mature immune cell types.
(A) Schematic cartoon of Xist RNA localization changes in developing B lymphocytes in bone marrow (top) and T cell progenitors in the thymus (bottom). Xist RNA is absent from the Xi in pro-B and DN1 progenitors, and transiently re-appears at the Xi during differentiation. (B) Diversity of Xist RNA localization patterns in immune cell progenitors and seven different mature immune cell types. Xist RNA is not detectable by RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in naïve follicular (FO) B cells, naïve mature CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and p-DCs. In stimulated B and T lymphocytes, Xist RNA transcripts are tightly clustered to the Xi. Dendritic cells (DCs), bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs), and NK T cells have distinct and dispersed patterns of Xist RNA localization. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (p-DCs), resting and in vitro activated, always lack detectible Xist RNA signals. Red dots represent RNA FISH results for Xist RNA. Abbreviations: HSC (hematopoietic stem cell), CLP (common lymphoid progenitor), CMP (common myeloid progenitor), DN1-DN4 (double negative thymocytes stages 1–4), BMDM (bone marrow derived macrophage), m-DC (myeloid-Dendritic cell), NK T cell (Natural killer T cell), L-DC (lymphoid-Dendritic Cell), p-DC (plasmacytoid dendritic cell).