Fig. 1.
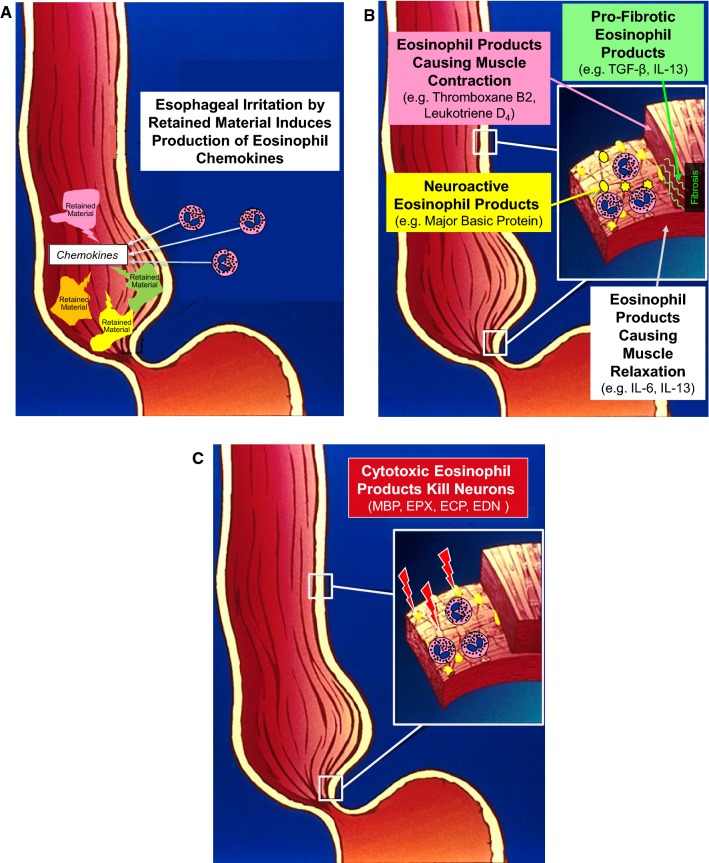
Potential mechanisms underlying the association of esophageal motility abnormalities and esophageal eosinophilia. a Primary esophageal motility abnormalities cause esophageal stasis with retained material that irritates the mucosa, inducing secretion of chemokines that attract eosinophils. b Motility abnormalities are caused by eosinophils in the esophagus that release myoactive, neuroactive, and pro-fibrotic eosinophil secretory products. c Motility abnormalities are caused by eosinophils in the esophagus that release cytotoxic eosinophil secretory products that destroy esophageal intramural neurons
Modified illustration of esophagus and stomach used with permission, copyright, American Gastroenterological Association Institute, Bethesda, MD, and figure reproduced from reference 27 with permission from the American Journal of Gastroenterology