FIG 8.
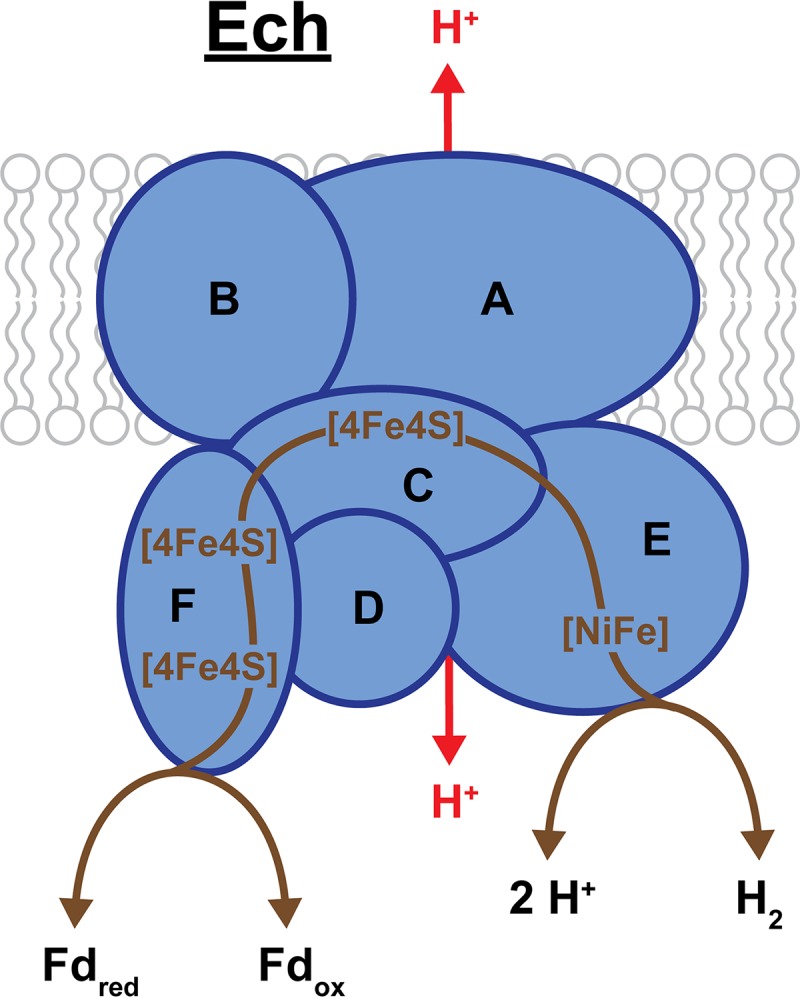
Ech of M. barkeri. Ech consists of 6 subunits (EchABCDEF), of which EchA and EchB are membrane bound and EchA is the likely location for H+ translocation (shown in red). The remaining 4 subunits are located in the cytoplasm and facilitate the transfer of electrons between Fd and H2/H+ by way of 3 cubane Fe-S clusters ([4Fe4S]). EchE contains the bimetallic [NiFe] active site for H2 formation/oxidation. Bidirectional arrows indicate Ech is a reversible enzyme, and brown lines trace the putative pathway of electron transport. In one direction, the exothermic oxidation of Fdred allows for internal H2 production and translocation of H2 to the outside of the cell.
