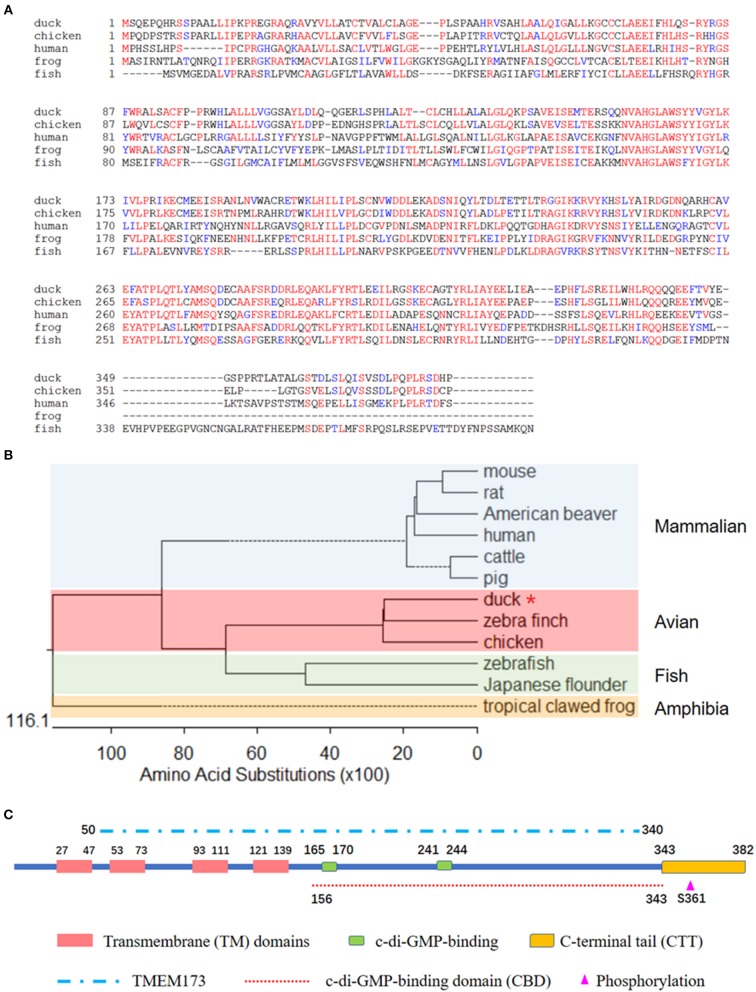
Figure 1.
(A) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of DuSTING with other animal STING proteins from the duck, chicken, human, frog, and fish. This was performed using the Clustal X program and edited with Boxshade. Red indicates amino acid identity and blue indicates similarity (50% threshold). (B) Phylogenetic tree of the deduced amino acid sequence of DuSTING and other animal STING proteins. The identified or predicted STINGs on the phylogenetic tree are sequences from different species available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The sequences were taken from GenBank entries, with accession numbers NP_082537.1 (mouse), NP_001102592.1 (rat), JAV42842.1 (American beaver), NP_938023.1 (human), NP_001039822.1 (cattle), AEL97644.1 (pig), XP_012430929.1 (zebra finch), NP_001292081.1 (chicken), BAU88509.1 (Japanese flounder), NP_001265766.1 (zebra fish), and NP_001106445.2 (tropical clawed frog). The number in the phylogenetic tree represents the bootstrap value. (C) The prediction of protein domains of duck STING.