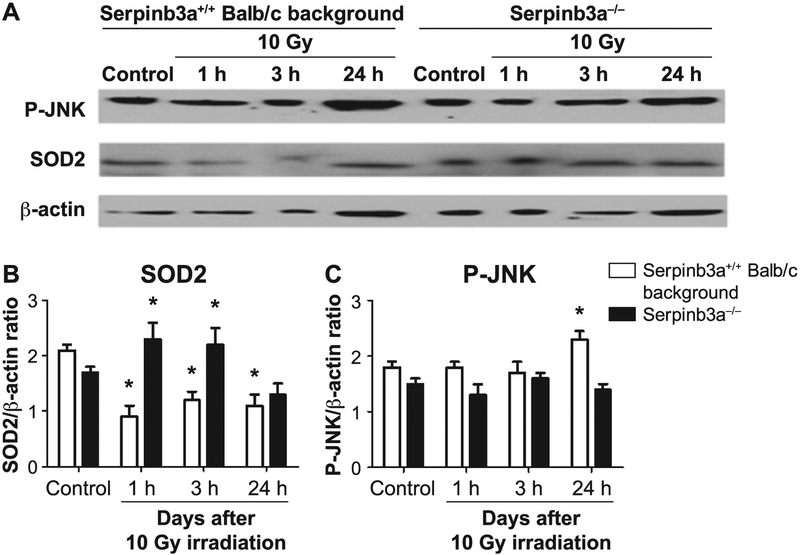
FIG. 7.
Western blot analysis of P-JNK and MnSOD (SOD2) protein after 10 Gy irradiation shows decreased radiation-induced P-JNK and increased MnSOD in Serpinb3a−/− compared to Serpinb3a+/+ Balb/c mouse bone marrow stromal cells. At 0, 1, 3 and 24 h after 10 Gy irradiation of Serpinb3a−/− and Serpinb3a+/+ Balb/c bone marrow stromal cells were collected, cells homogenized and Western blot analysis performed with antibodies to phosphorylated JNK and MnSOD. Panel A: After irradiation, Western blots showed increased P-JNK and decreased MnSOD levels in Serpinb3a+/+ Balb/c bone marrow cells. Panels B and C: Bar graphs quantitating MnSOD and P-JNK levels from Fig. 7A. Quantitation of MnSOD (panel B) performed by comparisons with bactin expression demonstrated that Serpinb3a−/− bone marrow stromal cells had increased MnSOD expression compared to Serpinb3a+/+ Balb/c bone marrow stromal cells. (*P < 0.0001 compared to control.) In contrast, as shown in panel C, JNK-phosphorylation, a marker of radiation-induced apoptosis, was significantly reduced in irradiated Serpinb3a−/− cell lines compared to Serpinb3a+/+ Balb/c bone marrow stromal cells. (*P = 0.0365 compared to control.)