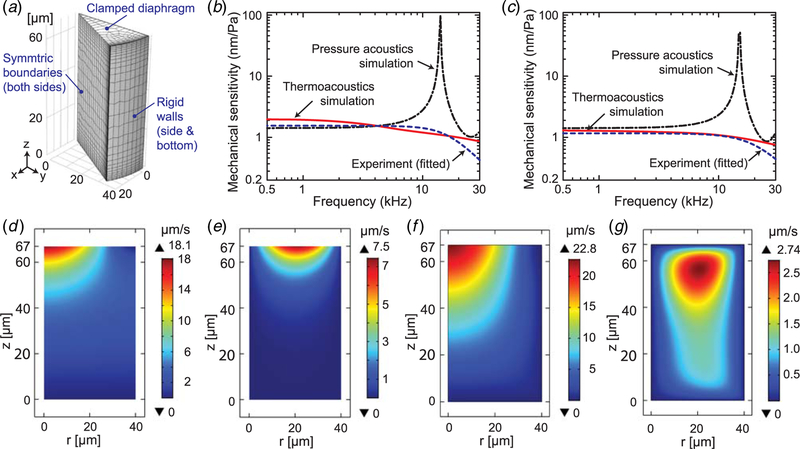
Fig. 4.
Numerical simulation to obtain the frequency response for the fabricated fiber optic sensors using COMSOL: (a) FEM model using COMSOL Multiphysics, (b) and (c) mechanical sensitivity as a function of frequency, comparing two kinds of FEM simulations with the experiment results, for the sensors with graphene-only films (b) and graphene–silver composite (c) films, (d )–(e) cross-sectional views of velocity fields (normal (d ) and tangential (e)) for the fiber optic sensor with graphene-only diaphragm at 2 kHz, obtained by using pressure acoustics simulation in COMSOL where loss is neglected, and (f) and (g) velocity fields (normal (f) and tangential (g)) for the same sensor and the same frequency as in (d )–(e) but obtained using thermoviscous acoustics simulation in COMSOL where thermal and viscous losses are considered