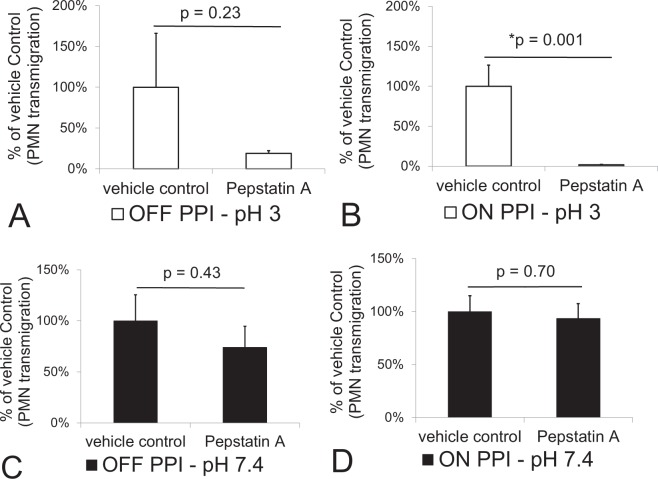
Figure 7.
Impact of Pepstatin A on neutrophil migration induced by patient gastric fluid samples set at pH 3 and pH 7.4. Pepstatin A (20 µg/ml) was added to gastric samples set at pH 3 and pH 7.4. Pepstatin A failed to significantly reduce the magnitude of neutrophil (PMN) migration across H292 lung epithelium induced by gastric samples set at pH 3 from patients off PPI therapy (A), but did significantly block neutrophil migration induced by gastric samples set at pH 3 from patients on PPI therapy (B). For gastric fluid samples set at pH 7.4, Pepstatin A failed to impact the magnitude of neutrophil migration induced by samples collected from patients off (C) and on (D) PPI therapy. A dilution of 1:4 in pH matched HBSS was used for all samples. Both on and off PPI therapy groups set at either pH 3 or 7.4 represent the mean +/− SEM of the average magnitude values (n = 3) of PMN migration by gastric fluid derived from 12 patients on PPI therapy and 12 patients off PPI therapy, diluted 1:4 in HBSS and treated with or without Pepstatin A (n = 12). Differences were considered significant between groups with and without Pepstatin A at p ≤ 0.05 and noted by the symbol (*). The p values were determined using an unpaired two-tailed student’s T test with equal variance within an internally controlled experiment. Panels A–D are representative internally controlled experiments conducted on at least two separate occasions yielding similar results.