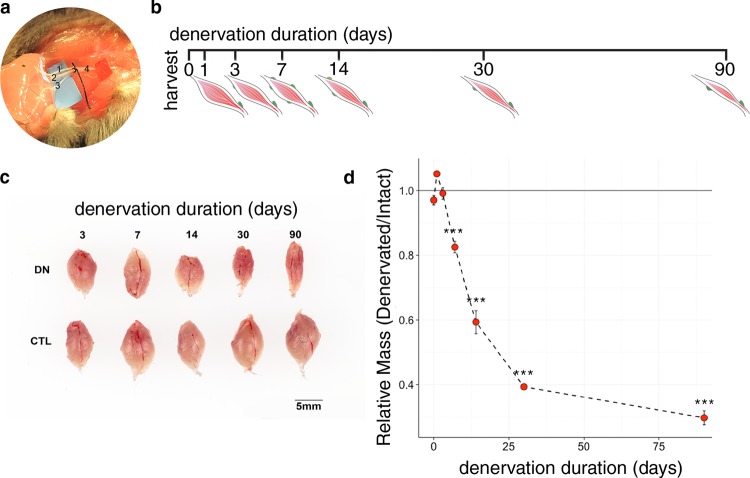
Fig. 1.
Overview of the experimental procedure. The tibial nerve, the largest branch of the sciatic nerve, supplies the gastrocnemius muscle and other muscles of the lower limb posterior compartment. In our mouse model of denervation atrophy, the sciatic nerve is identified, and its branches separated to isolate the tibial nerve (a; nerve identities are as follows: 1, sural nerve; 2, tibial nerve; 3, common peroneal/fibular nerve; 4, sciatic nerve). We generated a cohort of C57BL/6 J male mice denervated for 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, 30, or 90 days (b,c). Significant atrophy is apparent by 7 days after denervation, with consistent decline in mass during chronic denervation (d); ***P < 0.001 compared to baseline.