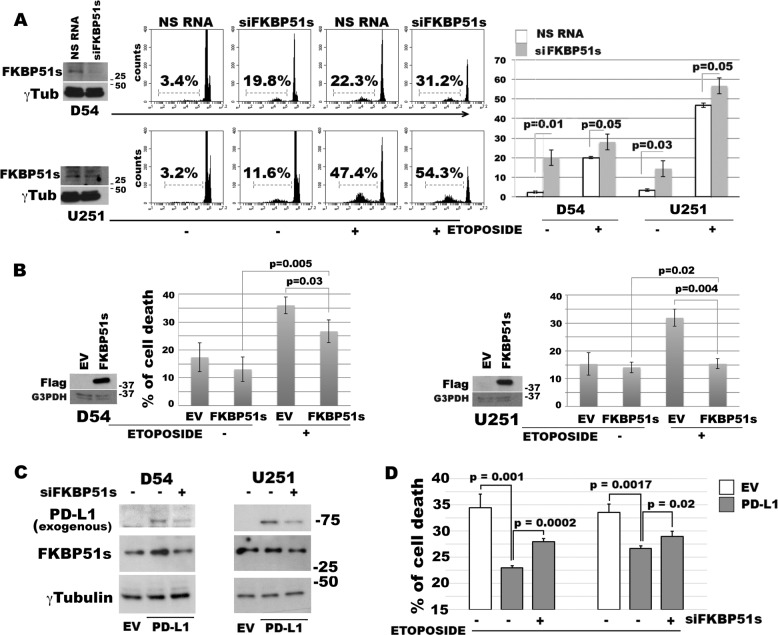
Fig. 2. FKBP51s regulates glioma cell death.
a Western blot assay of FKBP51s levels in D54MG and in U251MG silenced for FKBP51s. Cells were treated with FKBP51s siRNA or NSRNA for 24 h. Then, some of the cells were harvested for lysate preparation and some cells were treated with etoposide. After a further 24 h, cell death was measured. Representative flow-cytometric histograms of PI incorporation are shown along with graphical representations of means and standard deviations of cell-death values (N = 3). b Western blot assays of exogenous FKBP51s levels and graphical representations of means and standard deviations of cell-death values in D54MG and U251MG cells transfected with FKBP51s with EV- or FKBP51s-carrying plasmids (N = 3). Cells were treated with etoposide at 24 h from transfection. After a further 24 h, cell death was measured by flow cytometry (N = 3). c Western blot assays of the exogenous PD-L1-GFP level in D54MG and U251MG cells, silenced or not silenced for FKBP51s. Silencing of FKBP51s produced a decrease in PD-L1-GFP level in both cell lines. d D54MG and U251MG cells transfected with EV, PD-L1-GFP + NSRNA and PD-L1-GFP + FKBP51s siRNA, were treated with etoposide. After 24 h, cell death was measured using flow cytometry. FKBP51s depletion reduced the antiapoptotic effect of exogenous PD-L1. Each experiment was performed at least three times and in triplicate