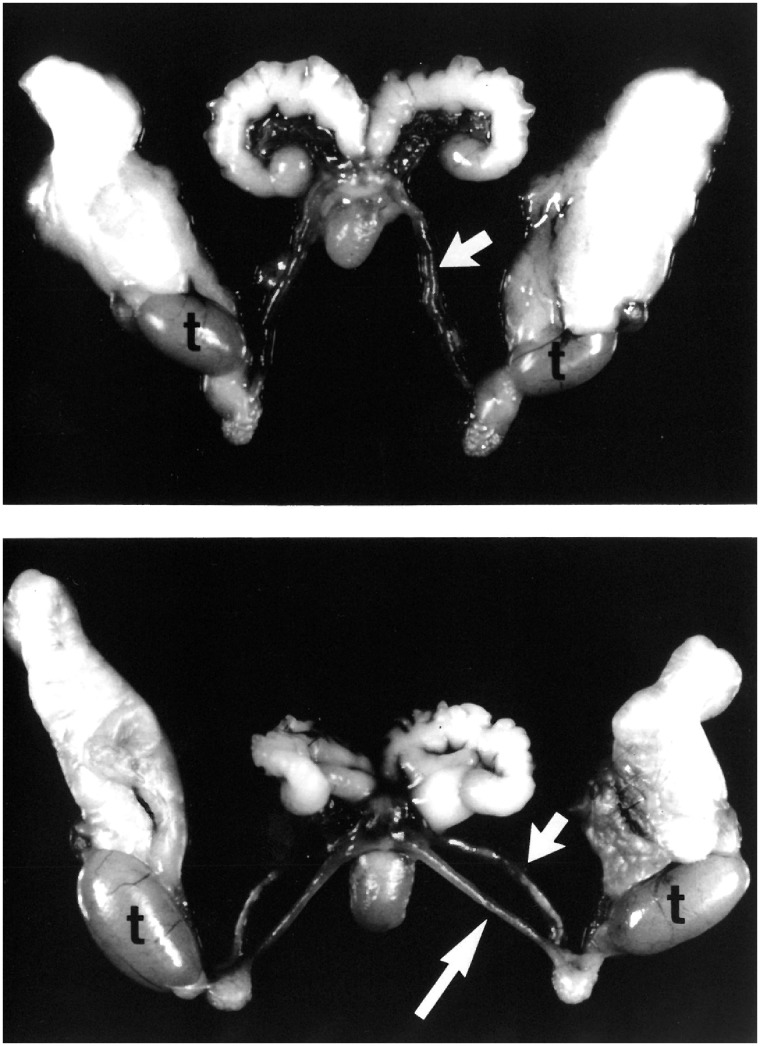
Figure 1:
PDMS in the mouse. Dissected reproductive tract organs from control (top) and Amh homozygous mutant (bottom) males. In the mutant, the uterine horns (long arrow) and vas deferens (short arrow) parallel each other down to the testes (t) because of a common connective tissue. In this dissection, the connective tissue has been cut to reveal the dual nature of the reproductive tract. Note that because of the physical constraints imposed by the vas deferens, the uterine horns project caudally instead of rostrally. Images from Behringer [21]