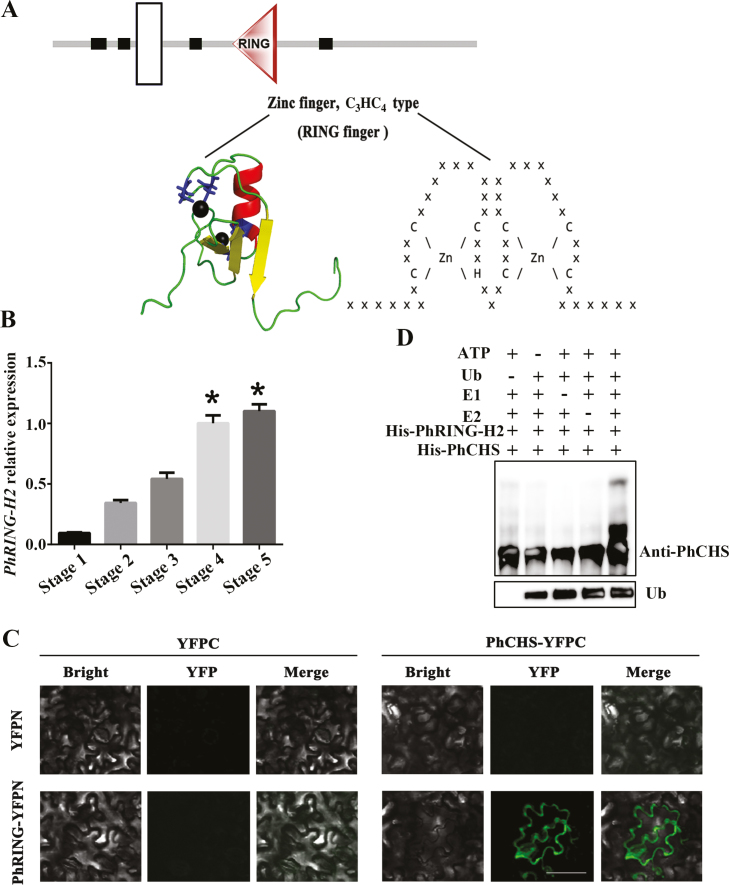
Fig. 7.
PhRING-H2 interacted with PhCHS and acted as an E3 ubiquitin ligase for ubiquitination of PhCHS in vitro. (A) Domain analysis of PhRING-H2. A RING finger domain is a structural domain of a zinc finger protein that contains a C3HC4 amino acid motif and binds two zinc cations. The structure prediction used the http://smart.embl.de/ website and tertiary structure prediction used the http://pfam.xfam.org website. White box indicates transmembrane region. Black boxes indicate low complexity region. Triangle indicates RING domain. (B) PhRING-H2 relative expression in petals during developmental stages (mean ±SD; n=3). (C) PhRING-H2 interacts with PhCHS in vivo. PhCHS fused with the C-terminus of YFPC (PhCHS–YFPC) was co-expressed with PhRING-H2 fused with the N-terminus of YFP (PhRING-H2–YFPN) in tobacco leaves. Images were collected after infiltration for 72 h. (D) PhRING-H2 acted as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of PhCHS in vitro. His–PhRING-H2 and His–PhCHS fusion protein were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified. His–PhRING-H2 fusion protein for E3 activity was measured in the presence or absence of ATP, ubiquitin, ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2), His–PhCHS, or ubiquitin (Ub). Protein bands with ubiquitin attached were detected with PhCHS antibody from immunized rabbit. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)