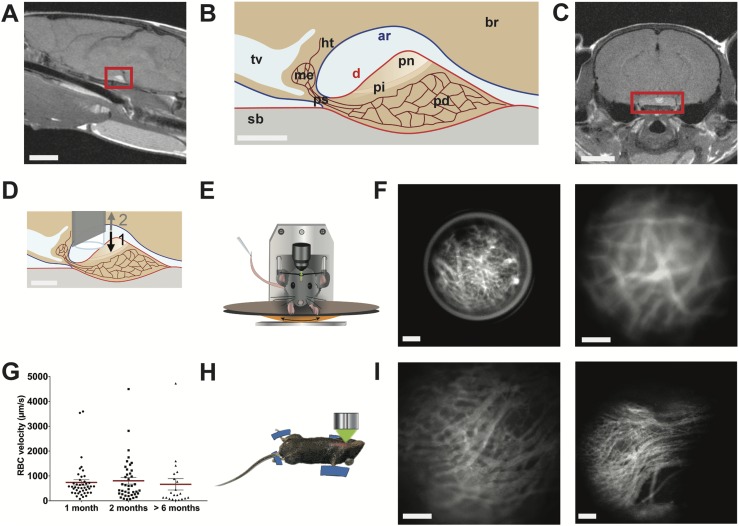
Figure 1.
In vivo imaging of pituitary blood flow in the awake mouse. (A) Sagittal MRI view of the midbrain from a female mouse. Red rectangle indicates pituitary location below the ventral side of the brain. Scale bar, 3 mm. (B) Drawing of a sagittal view of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Scale bar, 300 µm. (C) Coronal MRI view of the brain of a female mouse. Red rectangle indicates pituitary location. Scale bar, 3 mm. (D) Schema showing the GRIN lens implantation in the arachnoid matter region above the dorsal side of the pituitary. (1) Downward and (2) upward arrows indicate the sequential needle movements when the GRIN lens is positioned above the pituitary. Scale bar, 300 µm. (E) Head-fixed in vivo imaging of an awake mouse implanted with a GRIN lens, which provides an optical relay between the microscope and the pituitary gland. (F) Head-fixed in vivo imaging of the pituitary capillaries at low (left panel) and high (right panel) magnifications; representative image of n = 5 female mice. Scale bar, 100 µm. (G) Example of longitudinal monitoring of red blood cell (RBC) velocities in the same pituitary field viewed from 1 to 6 mo after GRIN lens implantation; n = 21 to 43 vessels analyzed per animal; n = 4 female mice. Also represented are means ± SEM (red lines). (H) Schematic arrangement of the ventral in vivo imaging approach in terminally anesthetized mice (12). (I) Ventral in vivo imaging of pituitary capillaries at the level of the pituitary parenchyma (left panel) and entrance (right panel) of different male mice. Scale bar, 100 µm. Data can be viewed in materials saved to an online repository (13). ar, arachnoid mater (in blue); br, brain; d, dura mater (in red); Ht, hypothalamus; me, median eminence; pd, pars distalis; pi, pars intermedia; pn, pars nervosa; ps, pituitary stalk; sb, sphenoidal bone; tv, third ventricle.