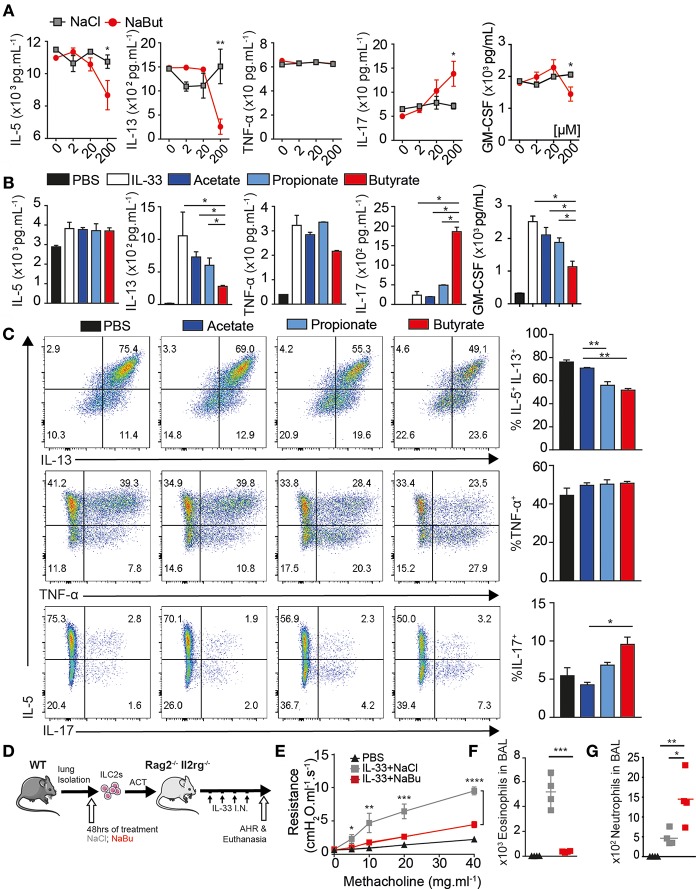
Figure 2.
Butyrate suppresses ILC2 function in-vitro and in-vivo. ILC2s were FACS purified from lungs of mice with or without 3 days 0.5 ug IL-33 administration i.n. as indicated and 5 × 103 cells/well-cultured ex-vivo for 2–3 days in the presence of IL-2 and IL-7, indicated salt at 2–200 uM and 10 ng/mL IL-33. (A) Schematic. (B) Dose dependence of ILC2 suppression by Sodium Butyrate compared to Sodium Chloride. (C) IL-5, IL-13, TNF-α, and IL-17a secretion in supernatant by activated ILC2 measured by Luminex after SCFA treatment at 200 uM. (D) Cytokine production by flow cytometry after 5 h stimulation with PMA/Ionomycin/BFA, comparing IL-5 and IL-13 (upper row), TNF-α (middle), or IL-17a in activated ILC2 after 3 days in-vitro. (E) Schematic, 5 × 104 ILC2 treated with 200 uM NaCl or Butyrate, washed, transferred i.v. into RAG−/−γC−/− mice challenged and with 3 days IL-33 i.n. (F) Lung resistance (AHR) upon increasing methacholine challenge. (G) Total Eosinophils in BAL. Total Neutrophil count in BAL. (A–D) Data are graphed as duplicate wells+-SEM, representative of three independent experiments and (E–G) two independent experiments, n = 4–5 mice/group+-SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.