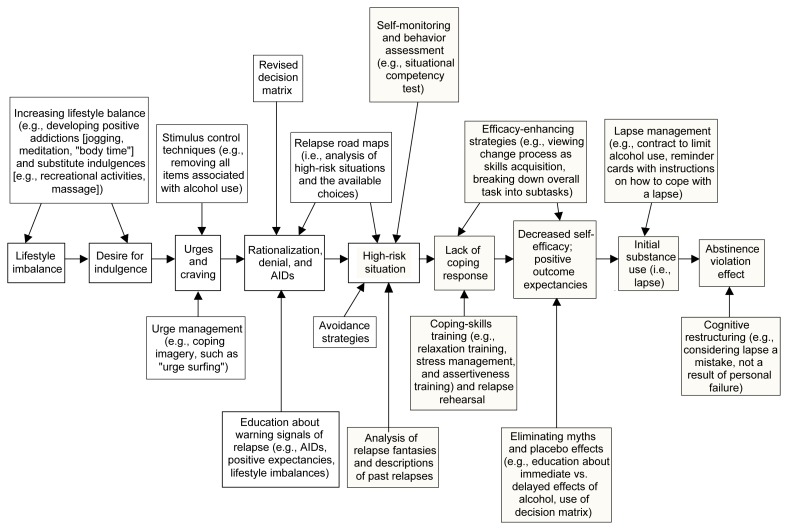
Figure 2.
Covert antecedents and immediate determinants of relapse and intervention strategies for identifying and preventing or avoiding those determinants. Lifestyle balance is an important aspect of preventing relapse. If stressors are not balanced by sufficient stress management strategies, the client is more likely to use alcohol in an attempt to gain some relief or escape from stress. This reaction typically leads to a desire for indulgence that often develops into cravings and urges. Two cognitive mechanisms that contribute to the covert planning of a relapse episode—rationalization and denial—as well as apparently irrelevant decisions (AIDs) can help precipitate high-risk situations, which are the central determinants of a relapse. People who lack adequate coping skills for handling these situations experience reduced confidence in their ability to cope (i.e., decreased self-efficacy). Moreover, these people often have positive expectations regarding the effects of alcohol (i.e., outcome expectancies). These factors can lead to initial alcohol use (i.e., a lapse), which can induce an abstinence violation effect that, in turn, influences the risk of progressing to a full relapse. Self-monitoring, behavior assessment, analyses of relapse fantasies, and descriptions of past relapses can help identify a person’s high-risk situations. Specific intervention strategies (e.g., skills training, relapse rehearsal, education, and cognitive restructuring) and general strategies (e.g., relaxation training, stress management, efficacy-enhancing imagery, contracts to limit the extent of alcohol use, and reminder cards) can help reduce the impact of relapse determinants. Shaded boxes indicate steps in the relapse process and intervention measures that are specific to each client and his or her ability to cope with alcohol-related situations. White boxes indicate steps in the relapse process and intervention strategies that are related to the client’s general lifestyle and coping skills. High-risk situations are related to both the client’s general and specific coping abilities.