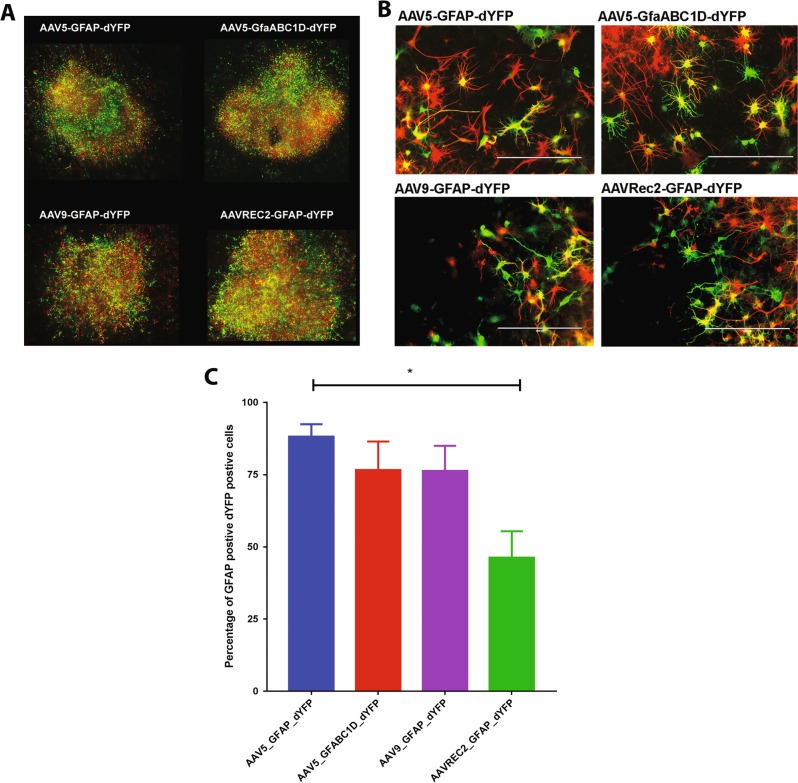
Fig. 2.
Organotypic slice cultures transduced with AAV vectors show robust gene expression and AAV5 results in the greatest astrocyte-tropic transductions. Spinal cord were excised from P10 to 15 rat pups, sliced and then cultured. Slices were transduced with AAV vectors: AAV5-GFAP-dYFP, AAV5-GfaABC1D-dYFP, AAV9-GFAP-dYFP, and AAVRec2-GFAP-dYFP (1 × 109 viral genomes each). Gene expression was developed for 7 days before fixing. Immunohistochemistry was used to visualised dYFP gene expression (green) and GFAP expression (red). a ×10 magnification images were stitched together to display the whole slice. b Images were captured on an EVOS FL Auto imaging station at ×20 magnification to analyse colocalisation of dYFP and GFAP. Images are representative images. c Data are represented as percentage of GFAP-positive dYFP-positive cell ± S.E.M. (n = 4 independent cultures; three technical repeats for each; three images per technical repeat) independent slice cultures. A one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used to determine statistical differences between the vectors, *P < 0.05