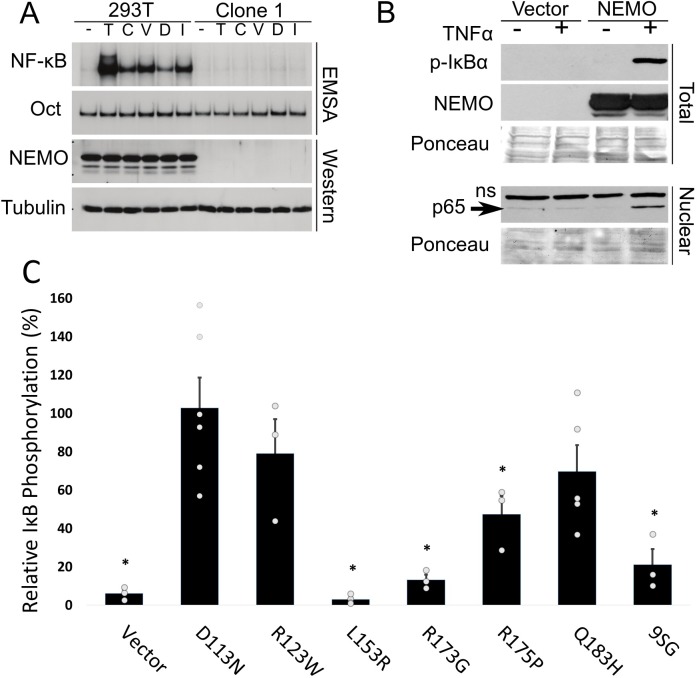
Fig 3. Clone 1 cells are defective for canonical NF-κB activation in response to multiple activators.
(A) Control 293T and clone 1 cells were treated with the indicated inducers of canonical NF-κB signaling, and extracts were then analyzed by EMSA for NF-κB and Oct1 DNA binding, or by Western blotting for NEMO and β-tubulin. Inducers are 10 ng/ml TNFα (T; 30 min), 10 μM camptothecin (C; 2 h), 10 μM VP16 (V; 2 h), 25 μM doxorubicin (D; 2 h) and 5 Gγ irradiation (I; 1.5 h). (B) Clone 1 cells were transfected with pcDNA-FLAG or pcDNA-FLAG-NEMO. Two days later, cells were treated with TNFα (+; 20 ng/ml for 10 min) or were left untreated (-). Western blotting of whole-cell extracts was done for phospho-IκBα or for NEMO (top) or nuclear extracts (bottom) were probed for NF-κB p65. ns, non-specific band. Ponceau staining of the filters was performed to ensure approximately equal loading of protein extracts. (C) Clone 1.1 cells were transfected with pcDNA-FLAG or expression vectors for the indicated NEMO proteins. As in (B), cells were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml for 10 min) and whole-cell extracts were probed for phospho-IκBα or NEMO. The amount of phospho-IκBα was then measured and is expressed relative to the amount of phospho-IκBα in cells transfected with wild-type NEMO in the same experiment. Values are the averages of at least three experiments. * p < 0.01, by Student’s t-test (as compared to wild-type NEMO).