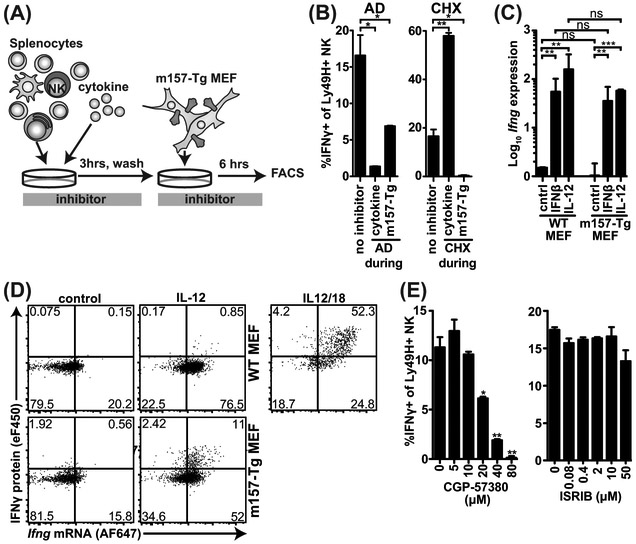
Figure 4: IL-12 and IFNβ induce Ifng mRNA whereas signaling through Ly49H initiates IFNγ translation.
(A) Experimental setup. (B) Splenocytes were pretreated with IL-12, hereafter the cells were washed and incubated with m157-Tg MEF in the presence of monensin. During IL-12 (cytokine) or m157-Tg stimulation transcription-inhibitor actinomycin D (AD; 2.5 μg/ml), or translation-inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX; 5 μg/ml) was added. (C) Splenic NK cells were purified by negative selection. 6 hours after stimulation with cytokines and/or m157-Tg MEF RNA was isolated from NK cells. Ifng transcripts were quantified using TAQman qPCR and normalized to Gapdh expression. (D) Purified NK cells were stimulated with IL12 and/or m157-Tg MEF for 6 hours and stained for IFNγ protein and Ifng mRNA using primeflow RNA assay. (E) Splenocytes were pretreated with IL-12, hereafter the cells were washed and stimulated with m157-Tg MEF in the presence of monensin and MNK-1/eIF4 inhibitor CGP-57380 or eIF2 inhibitor ISRIB at the indicated concentration. Representative experiment of 3 independent experiments is shown and each was performed in duplicate (B, E) or triplicate (C). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns= not significant.