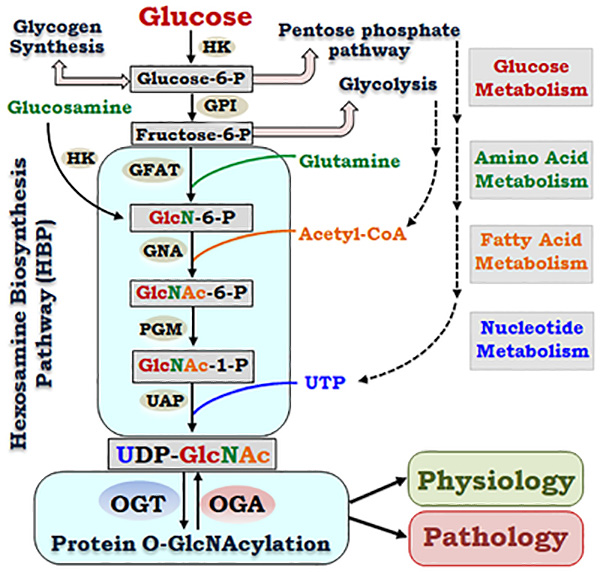
Figure 1. Glucose metabolism via hexosamine biosynthesis pathway links amino acid, fatty acid and nucleotide metabolisms to regulate cell physiology and pathology via protein O-GlcNAcylation.
In addition to glycolysis, glycogen synthesis and pentose phosphate pathway, glucose metabolism generates UDP-GlcNAc via the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP). The HBP utilizes a series of enzymes and substrates, which integrates glucose metabolism to amino acid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism and nucleotide metabolism. Dynamically regulated by the two enzymes, OGT and OGA, that catalyze the addition and removal of GlcNAc moiety on proteins respectively, O-GlcNAcylation affects a variety of cellular functions under physiological and pathological conditions. (HK: Hexokinase. GPI: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase. GFAT: Glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase. GNA: Glucosamine 6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase. PGM: Phospho-acetylglucosamine mutase, UAP: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase. OGT: O-GlcNAc transferase. OGA: O-GlcNAcase)