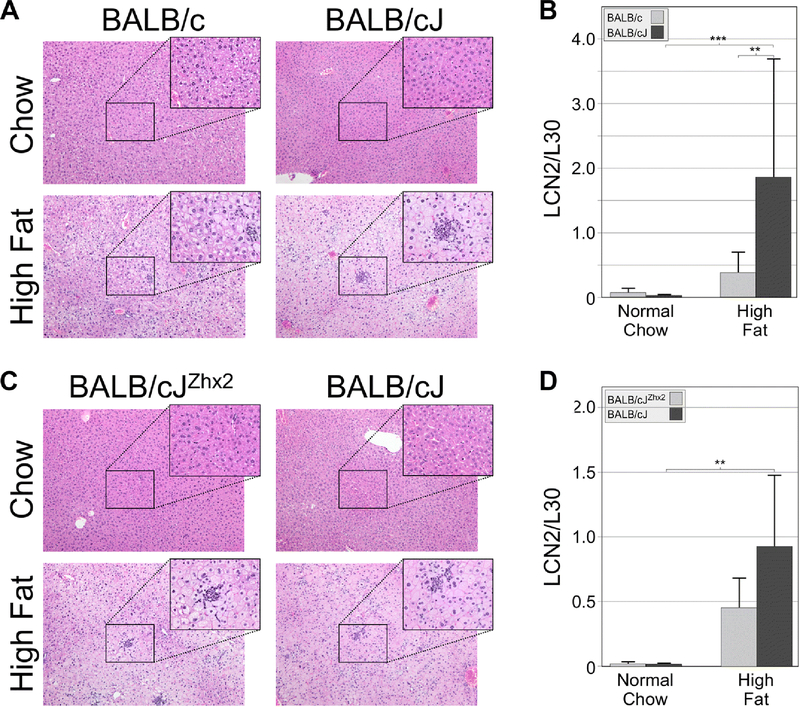
Figure 3. BALB/cJ livers exhibit greater hepatocyte ballooning and neutrophil infiltration than livers of BALB/c mice on a high fat chow.
A. H&E staining indicated that livers of BALB/cJ and BALB/c on a normal chow showed no abnormalities. When placed on a high fat chow, hepatocyte ballooning and neutrophil infiltration was greater in BALB/cJ than in BALB/c liver. B. Levels of LCN2 mRNA, a neutrophil marker, were low in both BALB/cJ and BALB/c mice on a normal chow and increased significantly in both substrains on a high fat chow; this high fat-induced increase was greater in BALB/cJ mice than in BALB/c mice. C. H&E staining indicated normal liver morphology in BALB/cJ mice with or without the TTR-Zhx2 transgene on a normal chow and no obvious difference in the degree of hepatocyte ballooning and neutrophil infiltration was observed between transgenic and non-transgenic mice on a high fat chow. D. LCN2 mRNA levels increased in BALB/cJ mice with or without the TTR-Zhx2 transgene on a high fat chow; although this increase was greater in non-transgenic animals, this difference did not reach significance. In both A and C, sections are shown at 10X; boxed regions are also shown at 40X; clusters of neutrophils are evident at 40X magnification. **p<0.1; ***p<0.01