Figure 1. HHcy and T2DM conditions reciprocally worsened each other, and combination of the two led to splenomegaly in male mice.
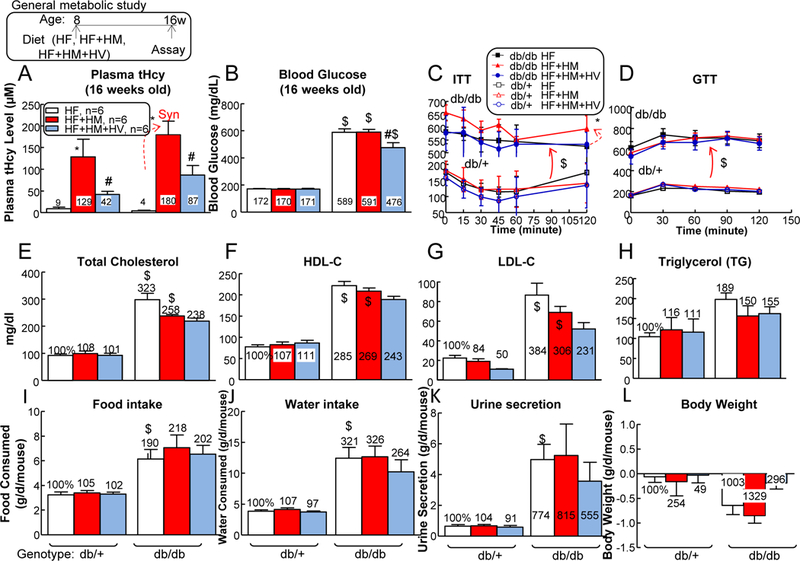
db/+ mice (non-T2DM groups) and db/db mice (T2DM groups) were fed a HF, HF+HM, or HF+HM+HV diet from 8 weeks old to 16 weeks old and then euthanized. Plasma was collected at the time of sacrifice. (A) Total plasma Hcy levels. Note that HF+HM diet increased plasma Hcy levels in db/+ mice, and further increased it in db/db mice. To evaluate mouse metabolism status systemically, all mice were subjected for blood glucose measurement (B), ITT (C), glucose tolerance test (GTT) (D), plasma total cholesterol (C) (E), HDL-C (F), LDL-C (G), and TG (H) measurements. Food intake (I), water intake (J), urine secretion (K), and body weight (L) changes were monitored in 24 hours at 16 weeks old. Each mouse was placed in the metabolic cages (HARVARD APPARATUS, Holliston, MA) for 24 hours prior to the experiment. After 24 hour accommodation, all the metabolism parameters were collected. N=6 mice. *P<0.05 vs HF diet mice with the same genotype, #P<0.05 vs HF+HM diet mice with the same genotype, $P<0.05 vs db/+ mice on the same diet. Synergy was defined as HHcy and T2DM produced a greater effects in HHcy+T2DM mice than the sum of that in HHcy and T2DM alone.
