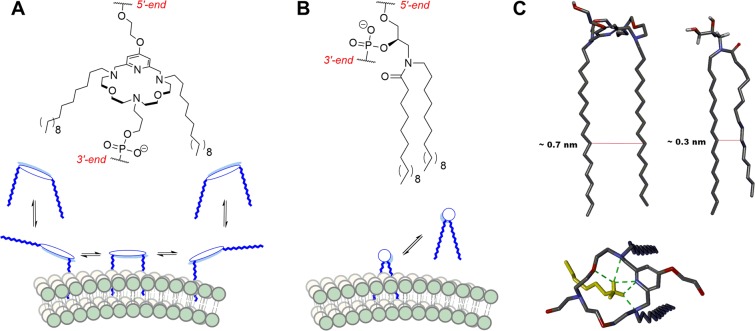
Figure 2.
Anchor design. Different anchor scaffold structures and proposed modes of anchoring (A) Anchor based on aza-crown ether scaffold has a 6-bond spacing over a rigid aromatic system giving the two lipophilic chains an approximate spacing of 0.7 nm and allowing each chain to interact with a different subset of lipids in the bilayer. (B) In the anchor based on 3-amino-1,2-propanediol scaffold both chains are attached to the same atom, favoring intramolecular interactions of the two chains, effectively resulting in a bigger lipophilic moiety which is expected to interact with the membrane in a concerted manner (C) Molecular representation of average lipid chain distances (red lines) for relaxed palmityl chains in aza crown ether and amino propanediol membrane anchors (hydrogens not shown for clarity) and top view of the aza crown ether macrocycle with hydrogen bonded (green dotted lines) ammonium head group of aminoethanol lipids from the lipid bilayer.