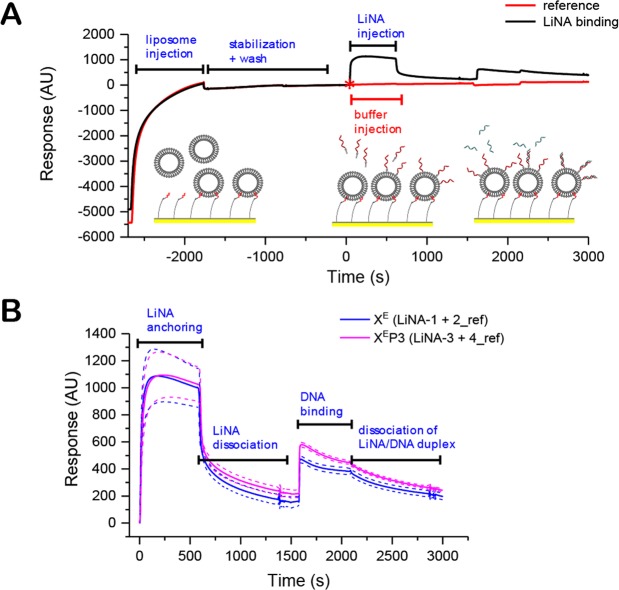
Figure 5.
SPR detection of LiNA-binding to immobilized liposomes. (A) Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) assay for detecting spontaneous binding of LiNAs to surface immobilized liposomes. After liposome capture (2 µl/min, 900 seconds), equilibration period (900 s) and buffer wash (20 µl/min) LiNA solution (5 µM in HBS, 600 s, 2 µl/min) or HBS (reference measurement) was injected followed by a dissociation phase under a flow of HBS (600 s, 2 µl/min). Then, complementary DNA (without lipid-modification) is injected in the same manner in both experiments. The complementary oligonucleotides showed no affinity to the liposomes on the sensor surface. The response and time axes of both runs are aligned at the point of LiNA injection (red asterisk) and the reference values subtracted. (B) Average response of LiNA-insertion for LiNA-1 (XE) and LiNA-3 (XEP3) and subsequent hybridization of complementary DNA to LiNA strands that remain bound to the surface after the dissociation phase. Measurements carried out at 25 °C, the solid line shows the mean signal of two injections, the dotted lines show the total error.