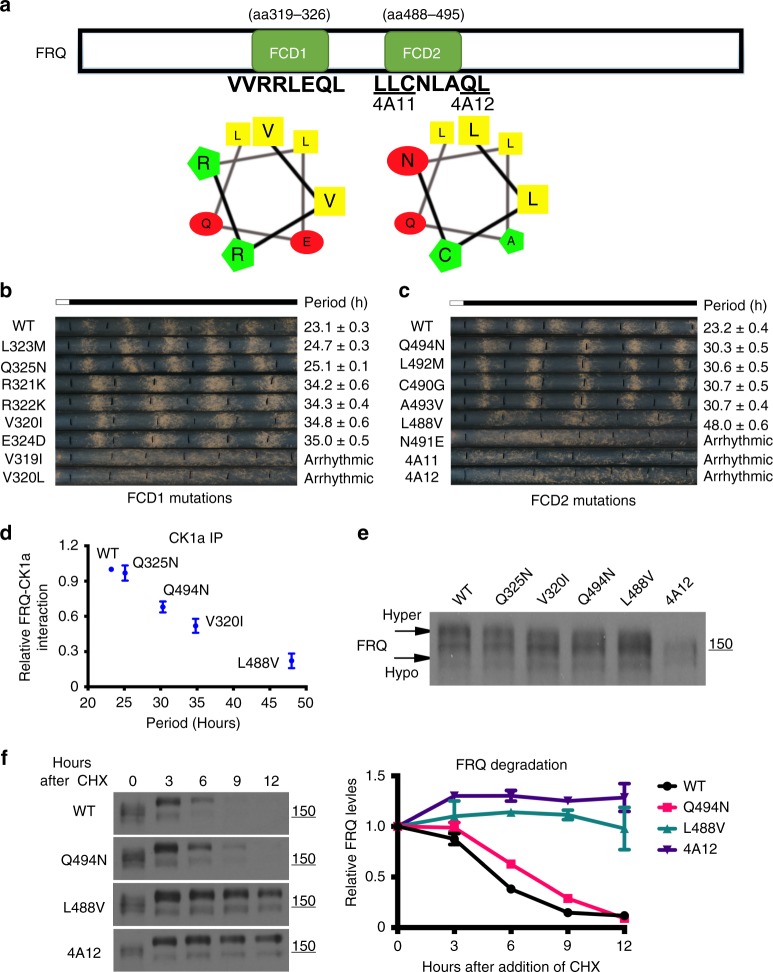
Fig. 2.
Dramatic impact on period by mutating the FCD domains. a A schematic diagram showing the FRQ FCD1 and FCD2 domains. The amino acid sequences within the domains that are critical for FRQ-CK1a interaction and helical representations are shown. The 4A11 and 4A12 mutations previously shown to completely disrupt the FRQ-CK1a interaction are indicated45. b, c Race tube assays showing the circadian conidiation rhythms and the period lengths of strains with mutation in b the FCD1 and c the FCD2 domains. Errors are standard errors of means (n = 5). d c-Myc immunoprecipitation assay showing that the amount of FRQ-Myc.CK1a in selected FCD period mutant strains relative to the amount in the wild-type strain. The strains were cultured in LL. Error bars are standard deviations (n = 4). e Western blot analysis comparing the FRQ phosphorylation profiles in the indicated strains. Strains were cultured in LL. Arrows indicates hyper- and hypo-phosphorylated FRQ. The position of the molecular weight marker is indicated. f Western blot analysis of FRQ in indicated strains after CHX treatment. Both hyper- and hypo-phosphorylated forms of FRQ are included in the quantification. The densitometric analysis is shown on the right. Error bars are standard deviations (n = 3). Source data are provided as a Source Data file