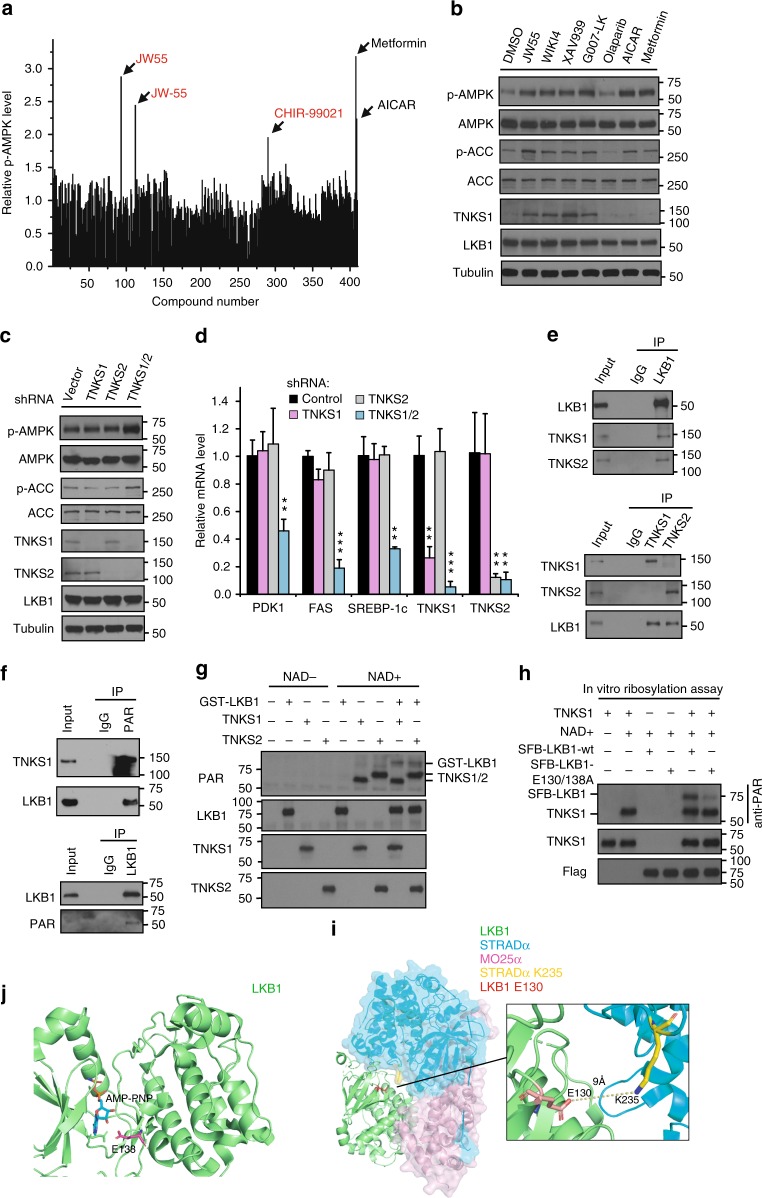
Fig. 1.
Tankyrases Regulate AMPK Activation through ribosylating LKB1. a Identification of the tankyrase inhibitor JW55 as an AMPK activator. A drug screen for regulators of AMPK was done by treating U2OS cells with a set of 406 drugs (the small-molecule Informer-Set contains 481 drugs, but we can only get 406 drugs from commercial sources) and metformin/AICAR. Both JW55 and JW-55 were the same compounds from two different commercial sources. b Tankyrase inhibitors specifically induce AMPK activation. HEK293A cells were treated with indicated inhibitors and proteins were detected by western blotting. c Double-knockdown of TNKS1/2 induces AMPK activation. HEK293A cells were transduced with the indicated shRNA and subjected to western blotting. d Depletion of TNKS1/2 suppresses expression of AMPK downstream glycolytic genes. Relative expression levels of PDK1, FAS SREBP-1c, and TNKS1/2 were detected by qPCR. e Interactions between endogenous LKB1 and TNKS1. Immunoprecipitation/western blotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. f LKB1 is ribosylated in vivo. Lysates from HEK293A cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation/western blotting assays. g LKB1 is ribosylated by TNKS1 in vitro. In vitro ribosylation was assessed by using recombinant TNKS1/LKB1 (E.coli purified GST-LKB1 and enzymatic active form of TNKS1, amino acids 1000–1328 with GST-tag). h E130 and E138 on LKB1 are key residues for TNKS1-induced ribosylation of LKB1. In vitro ribosylation was assessed by using the indicated proteins. i Structure view of LKB1/STRAD/MO25 complex. The LKB1-E130 residue is located close to the interface between LKB1 and STRAD. j Structure view of LKB1. The LKB1-E138 residue is located close to the ATP-binding pocket of LKB1. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001