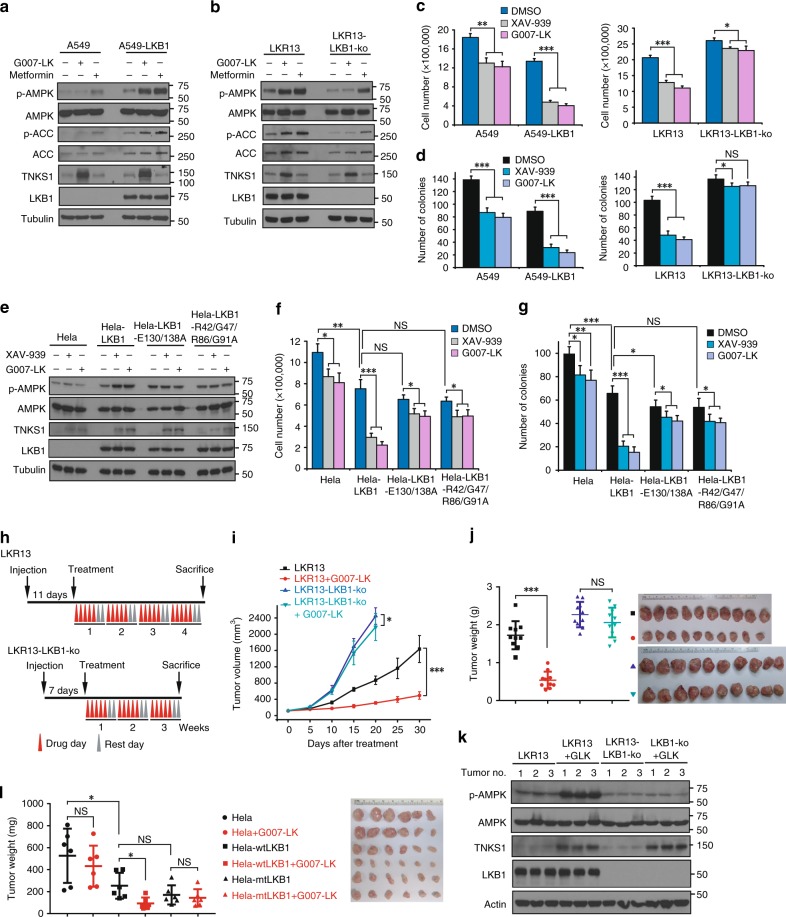
Fig. 2.
LKB1 is Essential for Tankyrase-Mediated AMPK Regulation. a Expression of LKB1 in LKB1-deficient A549 cells restores G007-LK-induced AMPK activation. b G007-LK induced AMPK activation is impaired in LKB1-knockout cells. LKR13 and LKR13-LKB1-knockout cells were treated with the indicated inhibitors were subjected to western blotting. c, d Tankyrase inhibitor–induced suppression of cell growth (c) and colony formation (d) depends on LKB1. Cell proliferation and colony formation were measured as described above; data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). e The LKB1-E130/138 A mutant is resistant to tankyrase inhibitor–induced AMPK activation. HeLa cells stably expressing wild-type LKB1 or the LKB1-E130/138 A mutant were treated with XAV939 or G007-LK and the cell lysates were subjected to western blotting. f, g Tankyrase inhibitors have much less of an effect on suppression of cell growth (f) and colony formation (g) in HeLa cells expressing the LKB1-E130/138 A mutant. Cell proliferation and colony formation were measured. h Schematic display of the LKR13 and LKR13-LKB1-knockout mouse xenograft experimental design. LKR13 (0.5 × 106 cells) and LKR13-LKB1-ko (0.25 × 106 cells) were implanted by injection. i, j Tumor volume (i) and weight (j) of mice from different treatment groups; data are presented as means ± SD (n = 10 mice). k Tumor proteins from the indicated groups of mice were extracted, and lysates were examined by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. l Tumor weight of mice with subcutaneous injection of 2 × 106 indicated HeLa cells (mtLKB1 indicates LKB1-E130/138 A mutant) with vehicle or G007-LK were presented (n = 6 mice, mean = ± SD). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001