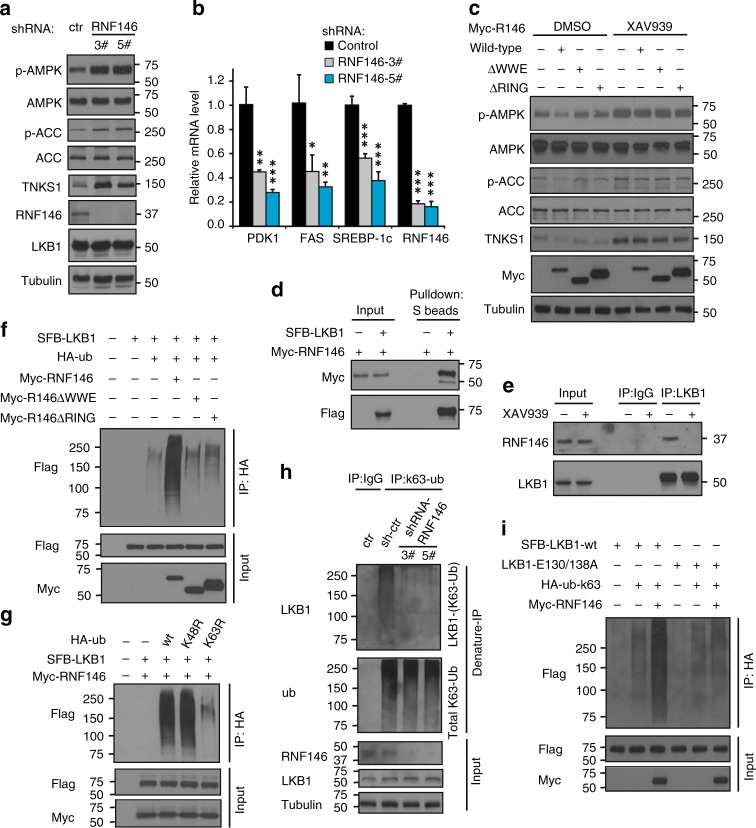
Fig. 3.
RNF146 is Involved in Regulation of the LKB1-AMPK Pathway Through K63-Linked LKB1 Ubiquitination. a Knockdown of RNF146 leads to AMPK activation. HEK293A cells were transduced with the indicated shRNA and subjected to western blotting. b Loss of RNF146 suppresses expression of AMPK downstream glycolytic genes. The relative expression levels of PDK1, FAS, and SREBP-1c were detected by qPCR. c, Both the WWE and RING domains of RNF146 are required for suppression of AMPK phosphorylation. d LKB1 interacts with RNF146. Myc-tagged RNF146 was co-expressed with or without SFB-LKB1 and cell lysates were subjected to pull-down assay. e Interaction between LKB1 and RNF146 is blocked by tankyrase inhibitor. f RNF146 induces LKB1 ubiquitination in vivo. In vivo ubiquitination assay was assessed in 293 T cells transfected with the indicated constructs followed by western blotting. g RNF146 promotes LKB1 ubiquitination through K63-linkage. 293 T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, and subjected to an in vivo ubiquitination assay. h RNF146 depletion diminishes K63-linked LKB1 ubiquitination. K63-linked ubiquitination of endogenous LKB1 was detected by denature-IP using a K63-specific ubiquitin antibody. i RNF146 doesn’t affect K63-linked ubiquitination of the LKB1-E130/138 A mutant. In vivo ubiquitination assay was performed in 293 T cells transfected with the indicated constructs. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001