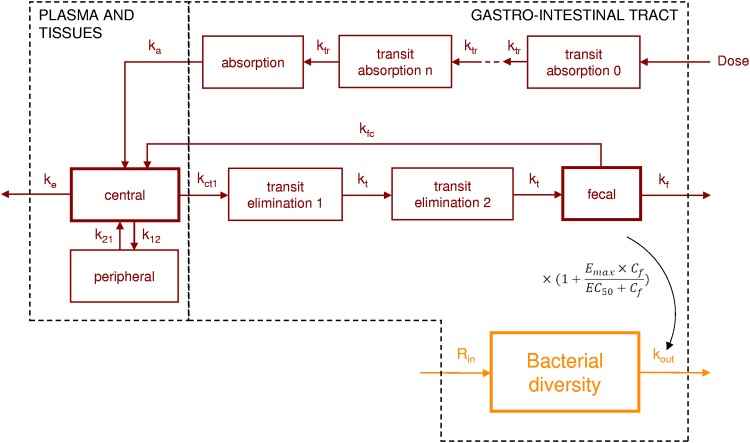
FIG 1.
Final compartmental model for plasma and fecal moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics (red) and for bacterial diversity indices (orange). ktr is the transfer rate between each compartment for the absorption delay; ka is the absorption rate to the central compartment; ke is the extraintestinal elimination rate from the central compartment; k12 and k21 are the transfer rates between the central compartment and the peripheral compartment; kct1 is the elimination rate from the central compartment to the intestinal tract; kfc is the transfer rate between the lower gastrointestinal tract and the central compartment; kt is the transfer rate between the intestinal transit compartments; kf is the elimination rate from the lower gastrointestinal tract; Rin is the zero-order constant for production of the diversity index; kout is the first-order elimination rate of the diversity index from the lower gastrointestinal tract. Cf is the concentration in the feces; Emax is the maximal effect of moxifloxacin on the elimination rate of the diversity index; and EC50 is the concentration of moxifloxacin leading to 50% of the maximal effect. Data were available for the 3 compartments with bold boxes. GIT, gastrointestinal tract.