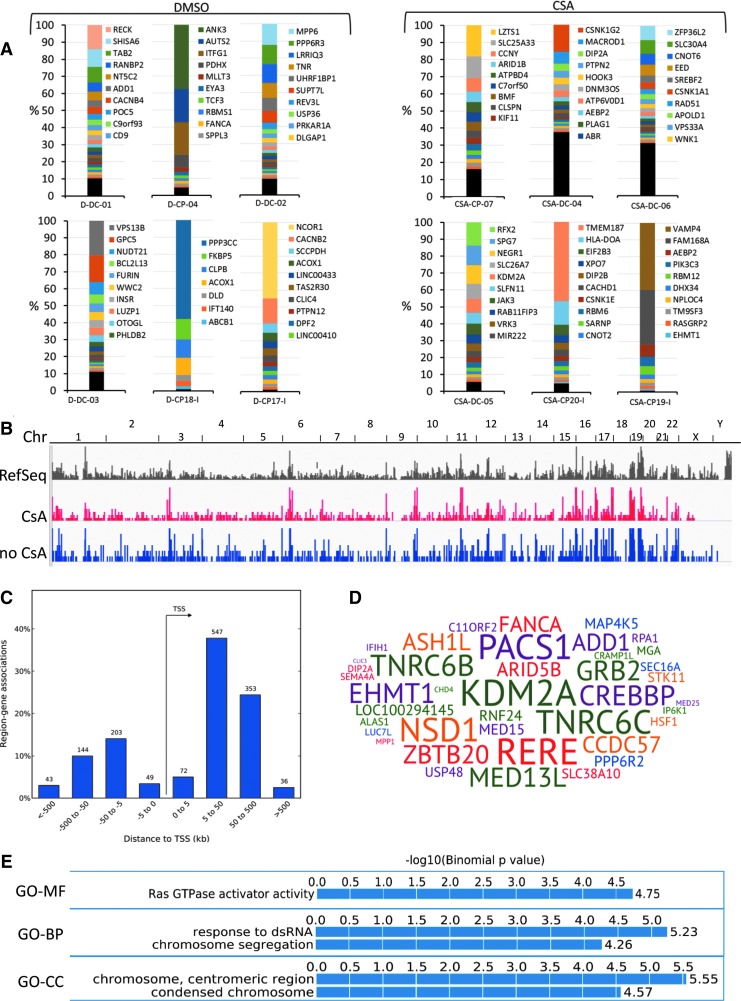
Figure 2.
Integration site analysis in HSPC transduced in the presence or absence of CsA. (A) Bar-plot representation of clonality and clonal abundance in BM cells harvested from NSG mice 17 weeks after transplant with human CD34+ cells transduced in the presence or absence of CsA (indicated as CsA and DMSO, respectively). Each color in the abundance bars represents the relative percent of integration sites with an abundance >1%; most abundant integrations are on top. Integration sites with an abundance <1% were pooled, and are represented in black at the bottom of each bar. The genes targeted by the 10 most abundant integration sites are indicated on the left of each bar (most abundant ranked from top to bottom). Mice D-CP18-I, D-CP17-I, CSA-CP20-I, and CSA-CP-19-I were transplanted with HSPC transduced with the IDUA-LV, while the remaining mice were transplanted with SINLV-green fluorescent protein (GFP). (B) Frequency distribution in chromosomes (indicated on top) of Ref Seq genes (in gray) and SIN-LV-GFP insertions in in vitro cultured HSPC after transduction in the presence of CsA (in red) or HSPCs in in vitro cultured HSPC transduced with the ARSA-expressing LV from a patient from the metachromatic leukodystrophy clinical trial (in blue; from Biffi et al.2). (C) Frequency distribution (y-axis, in %) of LV integration sites around gene transcription start sites (x-axis, in Kb). Above each bar, the number of integration sites landing in the specific interval is indicated. (D) Word cloud representation of the genes significantly over-targeted by common insertion site statistics in in vitro cultured HSPC after transduction with SINLV-GFP in the presence of CsA. The size of each gene symbol is proportional to the number of targeting LV insertions. (E) Enrichment analysis for ontological classes among the vector targeted genes performed by the Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool (GREAT). GO, gene ontology; MF, molecular function; BP, biological process; CC, cellular component.