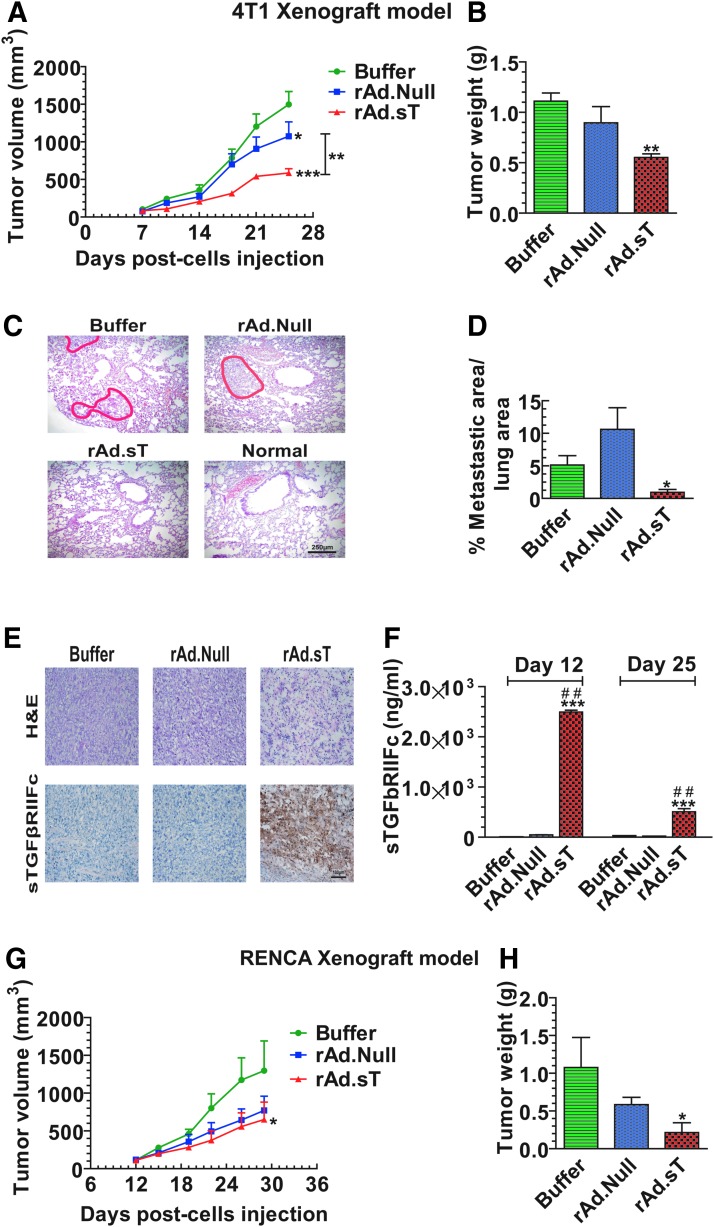
Figure 1.
Intratumoral inoculation of rAd.sT inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in mouse 4T1 and Renca tumor xenograft models. 4T1 cells were injected subcutaneously into the right flank (5 × 106 cells/mouse) of 4–6-week-old female BALB/c mice (day 0). On day 7, tumor-bearing mice were divided into three groups, buffer, rAd.Null, and rAd.sT groups (n = 10/group). rAd.sT, rAd.Null (2.5 × 1010 VPs/100 μL), or PBS was injected intratumorally. On day 10, a repeat injection was administered. On days 7, 10, 14, 18, 21, and 25, the tumor sizes were measured (A). On day 25, six mice from each group were euthanized, and the lungs and tumors were removed. Tumor weight was measured (B). The tumor metastasis lesions in lungs were detected by H&E staining. The representative images are shown in (C), and the metastatic areas in the lung were calculated (D). The tumor tissues were stained with (H&E) and also subjected to immunohistochemistry for detecting sTGFβRIIFc expression (E). On day 25, the sera were collected, and the sTGFβRIIFc protein was measured by ELISA (F). Renca cells were injected under the right flank (5 × 106 cells/mouse) of 4–6-week-old female BALB/c mice (day 0) to establish the subcutaneous renal model (n = 12/group). Tumors were treated with oncolytic adenoviruses as described above. The tumor sizes were measured at days 12, 15, 19, 22, 25, and 29 (G). On day 29, mice from each group were euthanized, and tumor weights were measured (H). Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 versus buffer group; ##p < 0.01 versus rAd.Null group. ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; sTGFβRIIFc, soluble transforming growth factor receptor II fused with human IgG Fc fragment; VP, viral particle.