FIGURE 10:
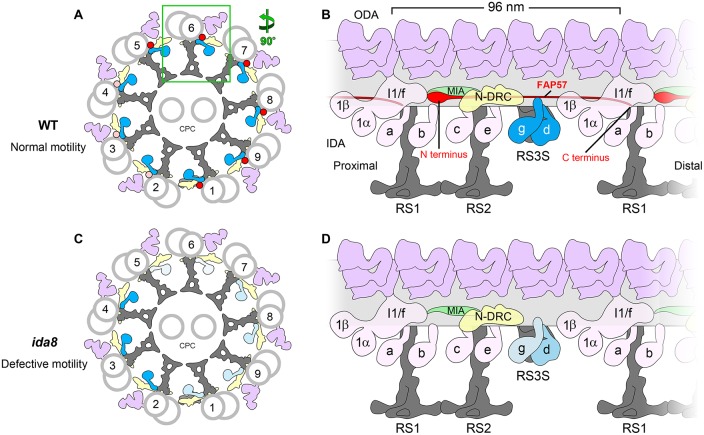
Model for the arrangement of FAP57 in the 96 nm repeat and its role in the assembly of certain IDAs. (A) Diagram of the cross-section of a WT axoneme showing the arrangement of the DMTs and the proposed asymmetric distribution of FAP57 across the nine DMTs: most FAP57 are located on DMTs 1, 5–9 (red dots), while a small number of FAP57 are also located on DMTs 2–4 (pink dots). (B) Diagram of the longitudinal view of a WT DMT showing the proposed location of FAP57. The N-terminal portion of FAP57 containing the WD repeat domains is proposed to form the more globular structure that is located distal to the IC/LC complex of the I1 dynein. The second half of FAP57 containing the coiled coil domains is proposed to extend along the surface of the DMT, passing through or adjacent to the bases of IDAs g and d, and then extend further, with its C terminus located close to the base of RS1. The IDAs g and d are highlighted in blue. Note that FAP57 is proposed to contact multiple structures implicated in the regulation of IDAs, including the IC/LC complex of the I1 dynein, the MIA complex, the N-DRC, and IDAs g and d. (C) Diagram of the cross-section of an ida8 axoneme showing the defects in the assembly of IDAs due to the loss of FAP57. In the absence of FAP57, fewer IDAs are assembled on DMTs 1, 5–9 (light blue) than on DMTs 2–4 (blue). (D) Diagram of the longitudinal view of an ida8 DMT showing the proposed role of FAP57 in stabilizing the assembly of specific IDAs. In the absence of FAP57, the assembly of IDA d is only slightly reduced but IDA g is significantly reduced. The observed increase in FBB7 may compensate in part for the absence of FAP57. The levels of IDA d and g are shown by the intensity of the blue labels, with the lighter blue hues indicating less dynein present. Other labels: ODA, outer dynein arm; IDA, inner dynein arm; N-DRC, nexin-dynein regulatory complex; CPC, central pair complex; RS3S, radial spoke 3 stand-in.