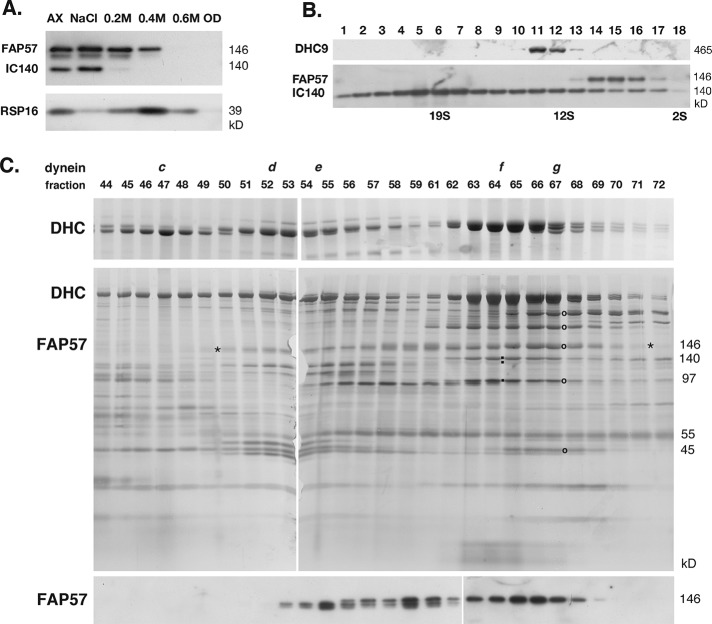
FIGURE 4:
Biochemical fractionation of FAP57 demonstrates coextraction and coelution with a subset of IDAs. (A) Western blot of WT axonemes (AX) and extracts obtained by sequential treatment with 0.6 M NaCl, 0.2 M, 0.4 M, and 0.6 M NaI, and the final pellet of extracted outer doublets (OD) was probed with antibodies against FAP57, the I1 dynein subunit IC140, and the RS subunit RSP16. (B) A dynein extract was fractionated by centrifugation on a 5–20% sucrose density gradient. Fractions 1–18 were analyzed on a Western blot probed with antibodies against DHC9, FAP57, and IC140. (C) A dynein extract from the outer arm mutant pf28 was fractionated by FPLC chromatography. Fractions 44–72 were analyzed by SDS–PAGE on 3–5% (top) and 5–15% (middle) gels stained with silver or on a Western blot (bottom) stained with the FAP57 antibody. FAP57 eluted in a broad region (see asterisks) that overlapped with the FPLC peaks of dyneins d, e, f, and g. The small black squares indicate the dynein ICs associated with I1/f dynein. The black circles indicate the bands in peak g that were analyzed by MS/MS.