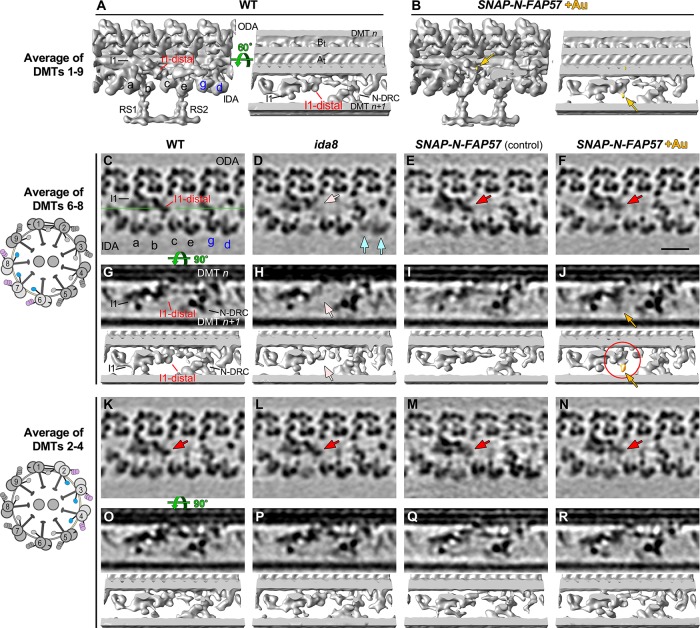
FIGURE 8:
Streptavidin-gold labeling, cryo-ET, and DMT specific averaging reveal the location of the N-terminus of FAP57. (A, B) Iso-surface renderings of the averaged 96 nm repeats from WT axonemes (A) or from streptavidin–gold–labeled axonemes from SNAP-N-FAP57 rescued strain (B). A new density was detected on the I1-distal structure in the gold-labeled rescued axonemes, as highlighted by yellow arrows. (C–F) Tomographic slices of the averaged 96 nm repeats of DMTs 6–8 from WT (C), ida8 (D), SNAP-N-FAP57 control (E), or gold-labeled SNAP-N-FAP57 axonemes (F; +Au). The SNAP-N-FAP57 control sample is different from the gold-labeled SNAP-N-FAP57 sample because the BG-(PEG)12-Biotin was omitted in the control during the labeling procedure. A diagram of an axoneme cross-section is shown on the left, with DMTs 6–8 highlighted in color. Defects in the I1-distal structure (pink arrows) and IDAs g and d (light blue arrows) were clearly visible as weaker densities in ida8 (D). These densities were restored in both of the rescued samples (red arrows; E and F). (G–J) Tomographic slices (top) and isosurface renderings (bottom) of averaged 96 nm repeat of DMTs 6–8 from WT (G), ida8 (H), SNAP-N-FAP57 control (I), or gold-labeled SNAP-N-FAP57 axonemes (J). The location of the tomographic slice is indicated by a green line in C. The red circle in J highlights the new density on I1-distal structure observed in the gold-labeled sample. This density is noticeably larger than that seen in the average of all nine DMTs in (B). (K–R) Images of averaged 96 nm repeats of DMTs 2–4 from WT (K, O), ida8 (L, P), SNAP-N-FAP57 control (M, Q), or gold-labeled SNAP-N-FAP57 axonemes (N, R). The I1-distal defect was hardly visible in the average of DMTs 2–4 of ida8 (L, P), and a new density was not clearly visible in the gold-labeled axonemes (N, R). Scale bar in F is 20 nm.