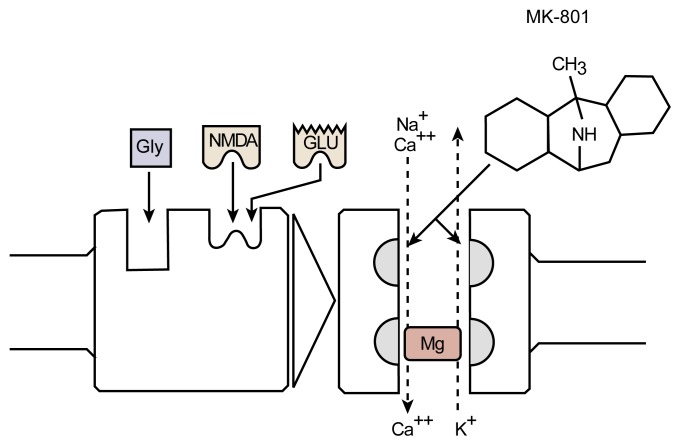
Figure 1.
The NMDA receptor complex. Activation (i.e., excitation) occurs when either glutamate (Glu) or N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine (Gly) bind to the receptor molecule. A channel within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg is removed from the channel and the receptor is activated, calcium (Ca++) and sodium (Na+) ions enter the cell and potassium ions (K+) leave. MK-801 prevents the flow of ions across the membrane by binding to a site within the ion channel, thereby blocking NMDA receptor function and protecting the cell against excess activation (i.e., excitotoxicity).