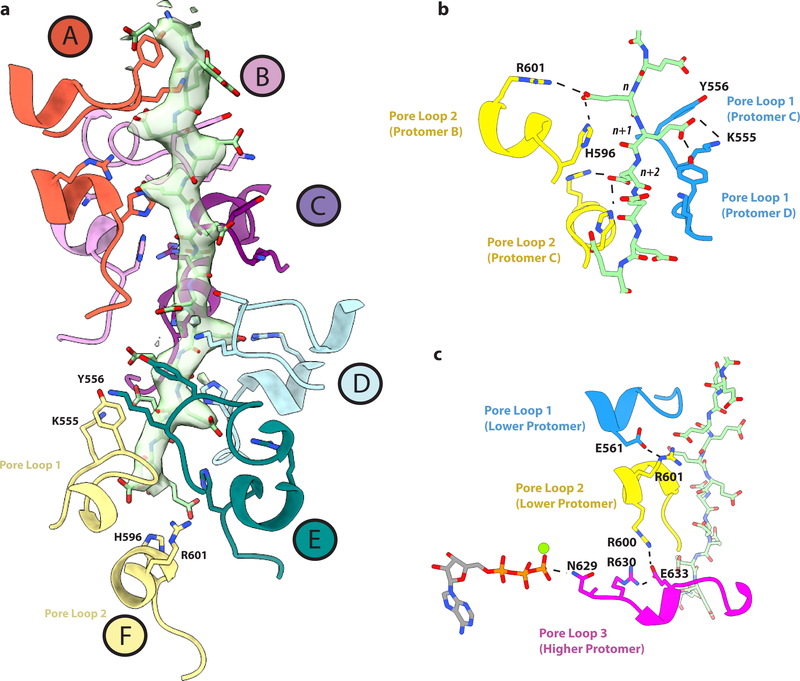
Figure 3. A pore loop network couples nucleotide binding to substrate engagement and oligomerization.
(a) Pore loops 1 and 2 interacting with the polyglutamate substrate. Substrate density is shown as a transparent surface with the polyglutamate model in light green. Pore loops are colored according to their assigned protomer, as in Figure 1. Residues that interact directly with the substrate (K555, Y556, H596, R601) are shown in stick representation. (b) Interactions between the substrate and conserved residues in pore loops 1 and 2. (c) A network of interactions between charged residues connects the peptide substrate to the nucleotide. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. All interactions depicted have a measured distance of less than 4 Å.