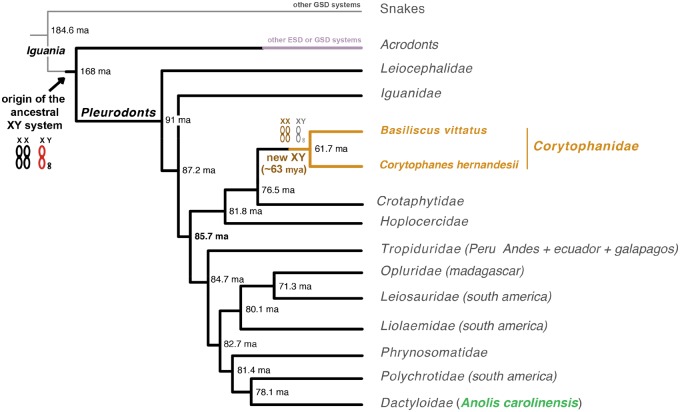
Fig. 1.
—Sex determination systems in the pleurodont clade. A tree representing the phylogenetic relationships between the families comprised in the pleurodont clade. The phylogenetic tree was based on Zheng and Wiens (2016). The estimate of Basiliscus vittatus and Corytophanes hernandesii divergence was taken from Taylor et al. (2017). Millions of years ago are denoted by “Ma.” Black and red XY chromosomes represent the pleurodont sex chromosome system, which originated in the ancestor of the infraorder Iguania. Most families in the pleurodont clade have conserved the same XY chromosomes; data based on Altmanova et al. (2018). This sex chromosome system has been well characterized in the green anole, Anolis carolinensis (highlighted in green), where it shows a highly degenerated Y chromosome and a male-specific X chromosome expression level upregulation; data based on Marin et al. (2017). The XY system in the Corytophanidae family originated 62.68 Ma (orange and gray XY chromosomes; results from this study). This corytophanid sex chromosome system is composed of heteromorphic sex chromosomes with a degenerated Y chromosome and an incomplete dosage compensation mechanism of the X chromosome in males.