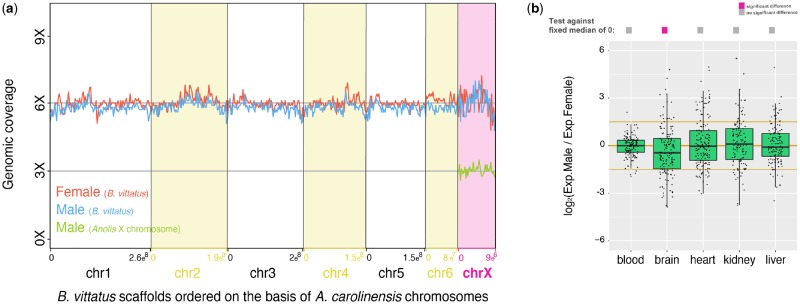
Fig. 2.
—Analysis of the pleurodont X chromosome in Basiliscus vittatus. (a) Coverage analyses using either male (blue line) or female (red line) genomic reads for the six main autosomes and the pleurodont X chromosome. Autosomes and the pleurodont X chromosome in B. vittatus were assembled on the basis of Anolis carolinensis reference genome. The expected coverage of an X chromosome in males with heteromorphic XY chromosomes is exemplified by the genomic coverage of the X chromosome in A. carolinensis (green line); genomic data for A. carolinensis were taken from Marin et al. (2017). (b) Boxplots representing the male/female expression ratio of genes located on the pleurodont X chromosome (n = 218 genes) in somatic tissues. Significant differences (Mann–Whitney U test): Benjamin–Hochberg-corrected P < 0.05 of temperatures against a distribution with fixed median of 0 (i.e., similar expression levels of X genes in males and females). Gray filled squares denote nonsignificant differences between male/female ratios of X genes against a distribution with fixed median of 0, whereas pink filled squares denote significant differences. Error bars, maximum and minimum values, excluding outliers.