Fig. 7.
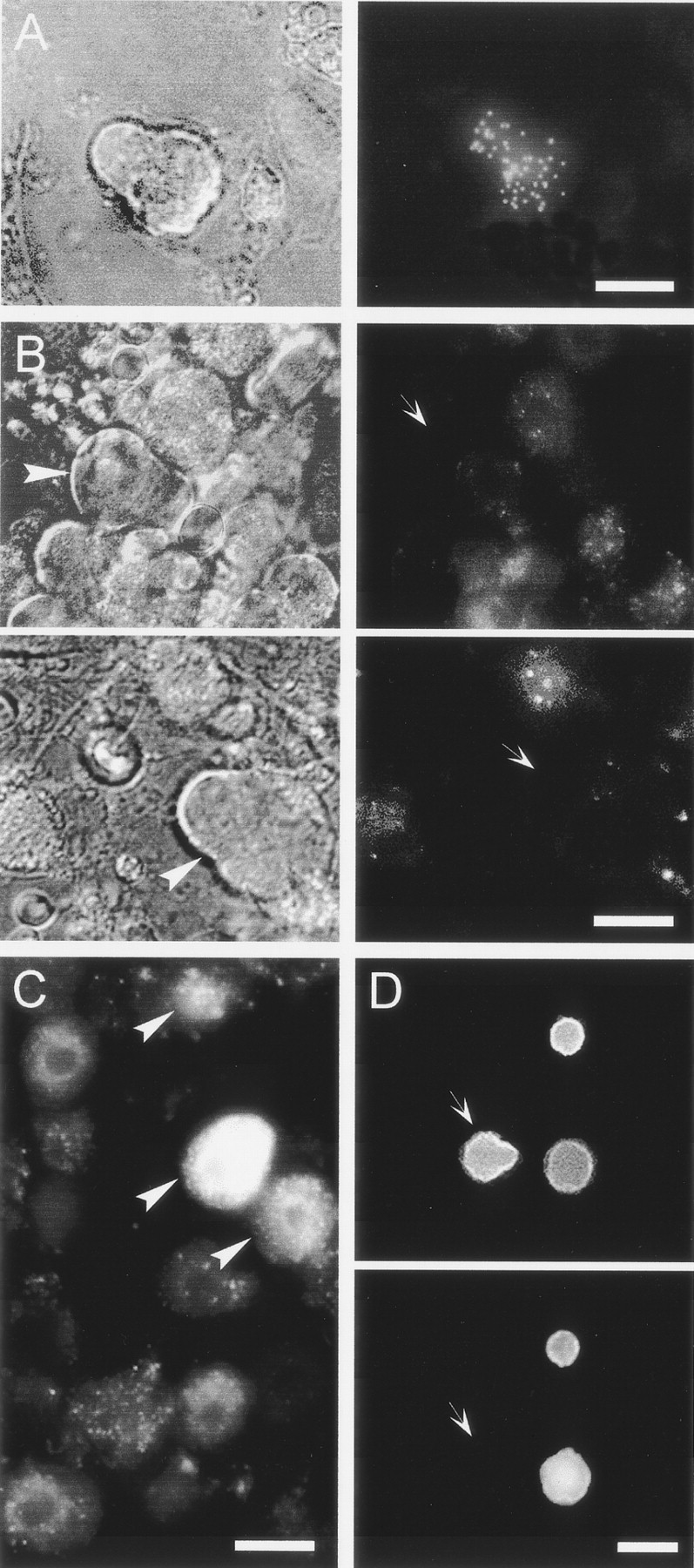
Peripheral target innervated by P-neurons as revealed by the retrograde transport of the lipophilic fluorescent neuronal tracer DiI (1%) injected into several tissues of newborn rats (P2). Cultures of DRG were examined for fluorescently labeled neurons (arrowheads) 3–4 d after a single injection of DiI.A, Phase contrast Nomarski photograph (left) and patchy pattern of DiI labeling (right) of the same P-neuron after the injection of a single 2 μl of DiI in the main muscle mass of both hindlegs.B, Dye injections into skin or subcutaneous targets never labeled P-neurons. Phase contrast photographs of two P-neurons (left, arrowheads) lacking DiI labeling (right, arrows) after large DiI injections at high concentration into several cutaneous sites of a rat.C, Round sensory neurons from the same animal in B labeled with DiI. Round labeled neurons (arrowheads) were also observed after injecting a very small volume (3 μl) of a low concentration of DiI into a single cutaneous site (data not shown).D, Photographs of the same view field after the treatment with antibodies against the β-tubulin isotype III (top) and the 200 kDa neurofilament protein (bottom). P-neurons showed no immunoreactivity for the 200 kDa neurofilament (arrows), whereas some round neurons were labeled. All neurons were positive for the β-tubulin isotype III, which clearly delineated the soma shape. Scale bars:A, D, 20 μm; B, 18 μm;C, 15 μm. The data were replicated three to four times.
