Fig. 2.
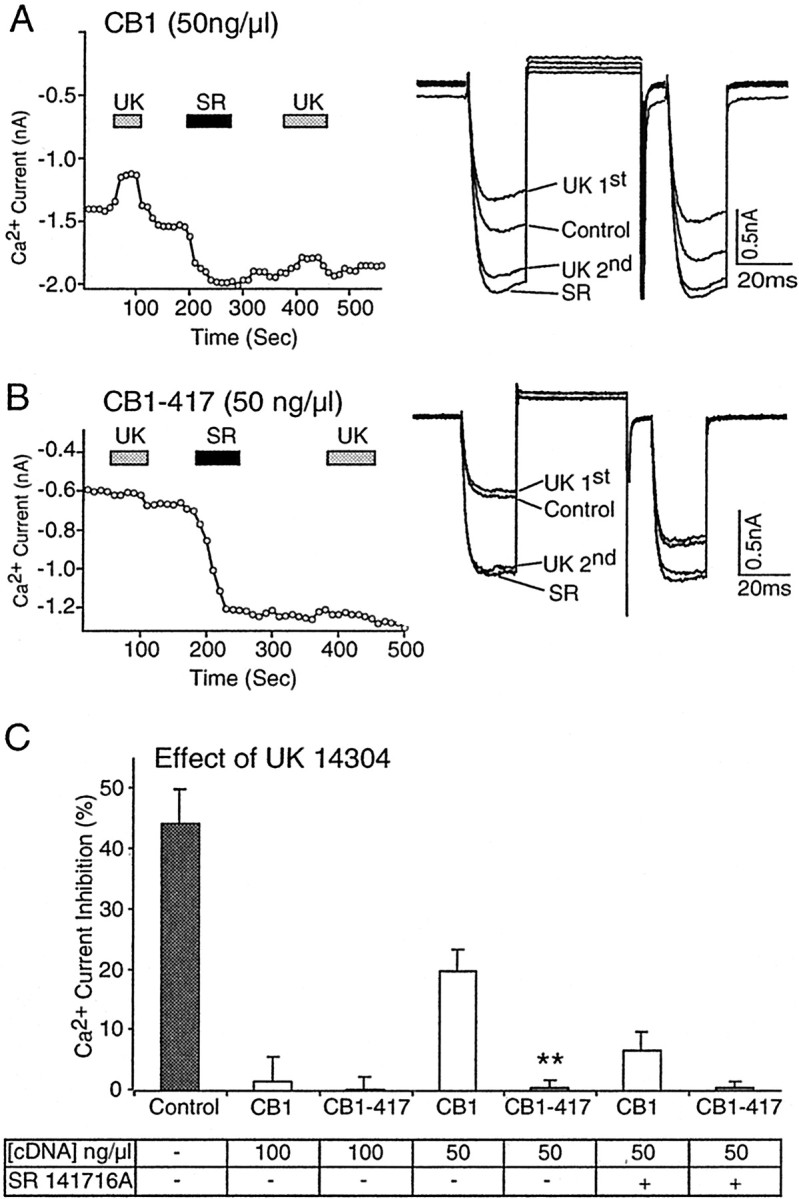
G-protein sequestration is enhanced by truncation of the distal C-terminal tail of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor.A, Left, In an SCG neuron that was injected with 50 ng/μl CB1, the cDNA application of the α2-adrenergic agonist UK 14304 (UK) produced a small inhibition of the Ca2+ current. Application of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor inverse agonist SR 141716A (SR) increased the Ca2+ current and blocked the effect of a subsequent application of UK 14304. A, Right, Superimposed current traces in the absence (Control) and presence of the first and second application of UK 14304 (UK) and SR 141716A (SR). B, Left, In an SCG neuron that was injected with 50 ng/μl CB1–417, cDNA application of UK 14304 had no effect on the Ca2+ current. Application of SR 141716A produced a large increase in the Ca2+current, and a subsequent application of UK 14304 also had no effect.B, Right, Superimposed current traces in the absence (Control) and presence of the first and second application of UK 14304 (UK) and SR 141716A (SR). C, Bar graph of Ca2+ current inhibition by UK 14304 in neurons expressing wild-type CB1 or truncated CB1–417 receptors from cDNA injections at the concentrations indicated in the table. The effect of UK 14304 in control neurons was abolished in neurons that were injected with 100 ng/μl CB1 or CB1–417 cDNA. The effect of UK 14304 was partially restored in neurons that were injected with 50 ng/μl CB1, but not with CB1–417 cDNA. The effect of UK 14304 was abolished after the application of SR 141716A for CB1-injected neurons (50 ng/μl). **p < 0.01 relative to wild-type CB1.
