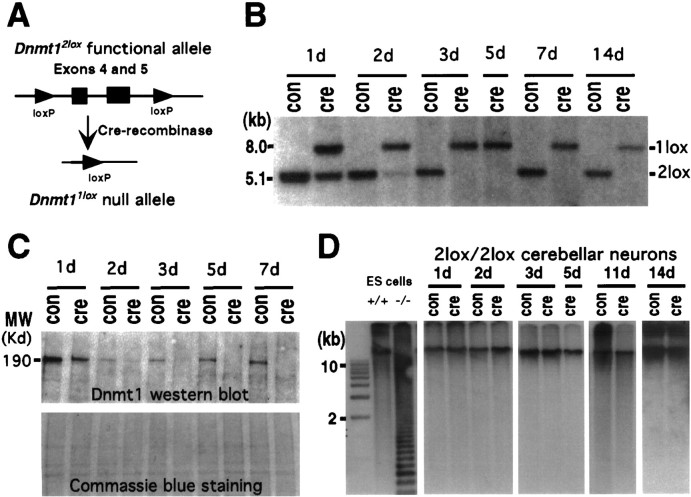
Fig. 1.
Conditional deletion of the Dnmt1gene in postmitotic cerebellar neurons. A, Schematic drawing of the cre/loxP-mediated Dnmt1 gene deletion. In the Dnmt12lox allele exons 4 and 5 were flanked by the 34 bp loxP sequence. In the presence of cre-recombinase the two loxP sites recombined, resulting in deletion of the exons and creation of theDnmt11lox null allele.B, P6 Dnmt12lox/2loxcerebellar dissociates were infected with recombinant adenovirus carrying the cre transgene at the time of plating and then were cultured for 1 d (1d) to 14 d (14d). DNAs were extracted from the cultures and digested with SpeI for Southern blot analysis of the efficiency of the Dnmt1 gene deletion in cerebellar cultures over time. The ratio of recombined null allele (1lox) over the sum of functionalDnmt12lox (2lox) and 1lox alleles indicates the efficiency of gene deletion.C, Western blot analysis of Dnmt1 proteins in control and mutant neurons. Top, Levels of Dnmt1 protein were detected with Dnmt1 antibodies in cultured cerebellar neurons with or without adeno-cre infection. Bottom, A duplicate gel was stained with Coomassie blue staining to show the equal loading of the protein extracts. D, Southern blot analysis of DNA methylation in cerebellar cultures. DNAs were digested with the methyl-sensitive enzyme HpaII, separated on agarose gel, transferred to the membrane, and hybridized with a centromeric minor satellite repeat probe. Small-molecular-weight fragments in Dnmt1 mutant embryonic stem cells indicate extensive demethylation of their DNA.