Fig. 3.
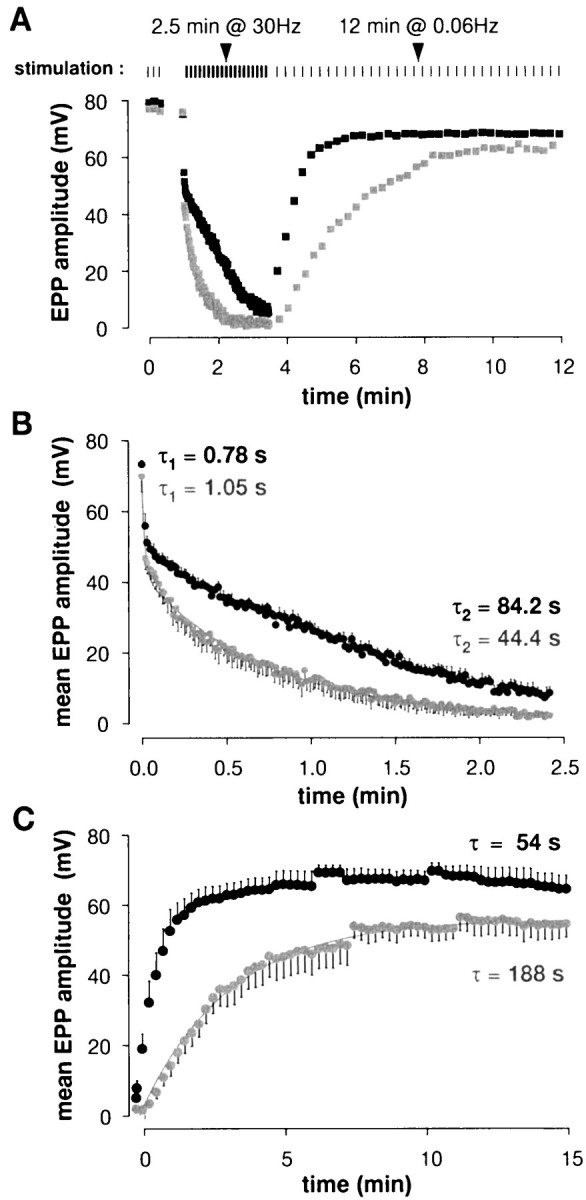
EPPs during and after tetanic stimulation were reduced significantly by staurosporine. A, Results from a typical experiment (protocol illustrated at top). During the 30 Hz train, EPP rundown was faster and recovery was slower at staurosporine-treated end plates (gray symbols) than in controls (black symbols).B, EPP rundown during tetanic stimulation. Shown are averages from five cells per condition. Double exponential fits gave time constants as shown on the graph; the main effect of staurosporine was to slow the second component by a factor of ∼2. C, EPP recovery after the tetanus (five cells per condition). The data are fit well with single exponentials; staurosporine slowed recovery by ∼3.5-fold.
