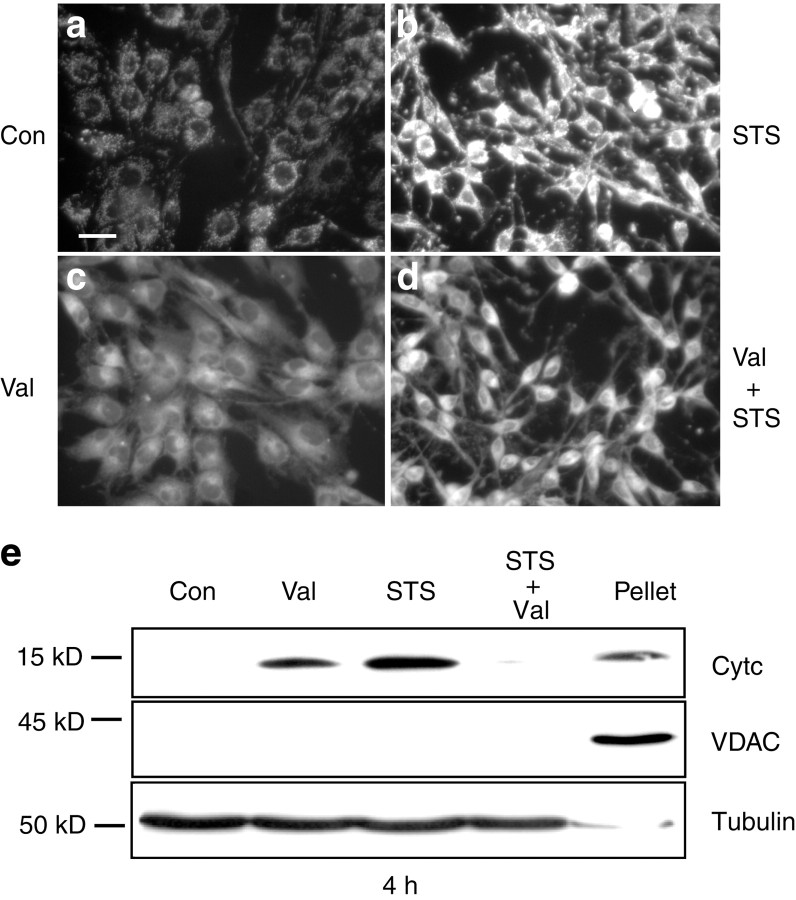
Fig. 8.
Valinomycin inhibits staurosporine-induced hyperpolarization and cytochrome c release. a–d, Cultures were exposed for 30 min to vehicle (Con) (a), STS (b), Val (c), or to a combination of STS and Val (d), loaded with 2 μm R123 for 30 min and washed with HBS. STS induced an increased uptake of R123 into mitochondria (b), whereas treatment with Val decreased R123 uptake into mitochondria (c). Combined exposure to STS and Val reduced the STS-induced increase in R123 uptake (d). Scale bar, 25 μm. Experiments were repeated four times with comparable results. e, Cultures were incubated for 4 hr with vehicle, Val, STS, or a combination of Val and STS. Cells were fractionated into a cytosolic and a mitochondria-containing nuclear–heavy membrane fraction (Pellet). Immunoblot analysis of cytosolic fractions was performed using an anti-cytochrome c antibody. Blots were incubated with an anti-VDAC antibody to exclude contaminations of the cytosolic fractions with mitochondria and with an anti-α-tubulin antibody to confirm equal loading of each sample. Control pellet of vehicle-treated cells is shown. The experiment was performed in triplicate and yielded comparable results.